A phase I study of the P-glycoprotein antagonist tariquidar in combination with vinorelbine
- PMID: 19417029
- PMCID: PMC7213754
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0938
A phase I study of the P-glycoprotein antagonist tariquidar in combination with vinorelbine
Abstract
Purpose: P-glycoprotein (Pgp) antagonists have had unpredictable pharmacokinetic interactions requiring reductions of chemotherapy. We report a phase I study using tariquidar (XR9576), a potent Pgp antagonist, in combination with vinorelbine.
Experimental design: Patients first received tariquidar alone to assess effects on the accumulation of (99m)Tc-sestamibi in tumor and normal organs and rhodamine efflux from CD56+ mononuclear cells. In the first cycle, vinorelbine pharmacokinetics was monitored after the day 1 and 8 doses without or with tariquidar. In subsequent cycles, vinorelbine was administered with tariquidar. Tariquidar pharmacokinetics was studied alone and with vinorelbine.
Results: Twenty-six patients were enrolled. Vinorelbine 20 mg/m(2) on day 1 and 8 was identified as the maximum tolerated dose (neutropenia). Nonhematologic grade 3/4 toxicities in 77 cycles included the following: abdominal pain (4 cycles), anorexia (2), constipation (2), fatigue (3), myalgia (2), pain (4) and dehydration, depression, diarrhea, ileus, nausea, and vomiting, (all once). A 150-mg dose of tariquidar: (1) reduced liver (99m)Tc-sestamibi clearance consistent with inhibition of liver Pgp; (2) increased (99m)Tc-sestamibi retention in a majority of tumor masses visible by (99m)Tc-sestamibi; and (3) blocked Pgp-mediated rhodamine efflux from CD56+ cells over the 48 hours examined. Tariquidar had no effects on vinorelbine pharmacokinetics. Vinorelbine had no effect on tariquidar pharmacokinetics. One patient with breast cancer had a minor response, and one with renal carcinoma had a partial remission.
Conclusions: Tariquidar is a potent Pgp antagonist, without significant side effects and much less pharmacokinetic interaction than previous Pgp antagonists. Tariquidar offers the potential to increase drug exposure in drug-resistant cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
Van Tellingen, commercial research support, Xenoba Ltd. The other authors disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
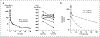
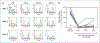
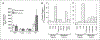
References
-
- Juliano RL, Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1976; 455:152–62. - PubMed
-
- Fojo A, Akiyama S, Gottesman MM, Pastan I. Reduced drug accumulation in multiply drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 1985;45:3002–7. - PubMed
-
- Beck WT, Mueller TJ, Tanzer LR. Altered surface membrane glycoproteins in Vinca alkaloid-resistant human leukemic lymphoblasts. Cancer Res 1979;39:2070–6. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent trans- porters. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Mistry P, Stewart AJ, Dangerfield W, et al. In vitro and in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a novel potent modulator, Tariquidar. Cancer Res 2001; 61:749–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

