EBV Zta protein induces the expression of interleukin-13, promoting the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines
- PMID: 19417211
- PMCID: PMC2710941
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-12-193375
EBV Zta protein induces the expression of interleukin-13, promoting the proliferation of EBV-infected B cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines
Abstract
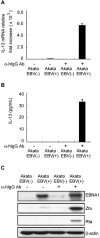
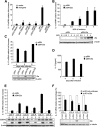
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection can modify the cytokine expression profiles of host cells and determine the fate of those cells. Of note, expression of interleukin-13 (IL-13) may be detected in EBV-associated Hodgkin lymphoma and the natural killer (NK) cells of chronic active EBV-infected patients, but its biologic role and regulatory mechanisms are not understood. Using cytokine antibody arrays, we found that IL-13 production is induced in B cells early during EBV infection. Furthermore, the EBV lytic protein, Zta (also known as the BZLF-1 product), which is a transcriptional activator, was found to induce IL-13 expression following transfection. Mechanistically, induction of IL-13 expression by Zta is mediated directly through its binding to the IL-13 promoter, via a consensus AP-1 binding site. Blockade of IL-13 by antibody neutralization showed that IL-13 is required at an early stage of EBV-induced proliferation and for long-term maintenance of the growth of EBV immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). Thus, Zta-induced IL-13 production facilitates B-cell proliferation and may contribute to the pathogenesis of EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders, such as posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) and Hodgkin lymphoma.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Maintenance of Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Status by a Novel Mechanism, Latent Membrane Protein 1-Induced Interleukin-32, via the Protein Kinase Cδ Pathway.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(11):5968-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00168-15. Epub 2015 Mar 25. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25810549 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of activation of the BNLF2a immune evasion gene of Epstein-Barr virus by Zta.J Gen Virol. 2018 Jun;99(6):805-817. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001056. Epub 2018 Mar 26. J Gen Virol. 2018. PMID: 29580369 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions involving cyclosporine A, interleukin-6, and Epstein-Barr virus lead to the promotion of B-cell lymphoproliferative disease.Leuk Lymphoma. 1996 May;21(5-6):379-90. doi: 10.3109/10428199609093435. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996. PMID: 9172802 Review.
-
The zta transactivator involved in induction of lytic cycle gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes binds to both AP-1 and ZRE sites in target promoter and enhancer regions.J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1143-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.64.3.1143-1155.1990. J Virol. 1990. PMID: 2154599 Free PMC article.
-
Human B cells on their route to latent infection--early but transient expression of lytic genes of Epstein-Barr virus.Eur J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;91(1):65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21450364 Review.
Cited by
-
The bZIP Proteins of Oncogenic Viruses.Viruses. 2020 Jul 14;12(7):757. doi: 10.3390/v12070757. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32674309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A formal analysis of cytokine networks in chronic fatigue syndrome.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 Oct;24(7):1209-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.04.012. Epub 2010 May 4. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 20447453 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A imposes sensitivity to apoptosis.J Gen Virol. 2010 Sep;91(Pt 9):2197-202. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.021444-0. Epub 2010 May 19. J Gen Virol. 2010. PMID: 20484564 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic EBV infection investigated by detection of Soluble Epstein-Barr virus ZEBRA in the serum of patients with PTLD.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 5;7(1):10479. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09798-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28874674 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antisense Transcripts and Antisense Protein: A New Perspective on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 12;11:625941. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.625941. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33510738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:757–768. - PubMed
-
- Hislop AD, Taylor GS, Sauce D, Rickinson AB. Cellular responses to viral infection in humans: lessons from Epstein-Barr virus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:587–617. - PubMed
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Fields virology. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb MA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE, editors. Epstein-Barr Virus. 4th Ed. Vol 2. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin; 2001.
-
- Torkildsen O, Nyland H, Myrmel H, Myhr KM. Epstein-Barr virus reactivation and multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2008;15:106–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

