The dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319 interacts with adaptor protein 2 and follows the classical clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway
- PMID: 19419997
- PMCID: PMC2711651
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00630.2008
The dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319 interacts with adaptor protein 2 and follows the classical clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway
Abstract
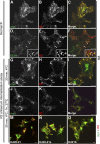
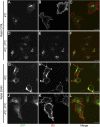
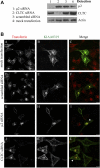
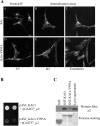
Recently, genetic studies have implicated KIAA0319 in developmental dyslexia, the most common of the childhood learning disorders. The first functional data indicated that the KIAA0319 protein is expressed on the plasma membrane and may be involved in neuronal migration. Further analysis of the subcellular distribution of the overexpressed protein in mammalian cells indicates that KIAA0319 can colocalize with the early endosomal marker early endosome antigen 1 (EEA1) in large intracellular vesicles, suggesting that it is endocytosed. Antibody internalization assays with full-length KIAA0319 and deletion constructs confirmed that KIAA0319 is internalized and showed the importance of the cytoplasmic juxtamembranal region in this process. The present study has identified the medium subunit (mu2) of adaptor protein 2 (AP-2) as a binding partner of KIAA0319 in a yeast two-hybrid screen. Using Rab5 mutants or depletion of the mu-subunit of AP-2 or clathrin heavy chain by RNA interference, we demonstrate that KIAA0319 follows a clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway. We also identify tyrosine-995 of KIAA0319 as a critical amino acid required for the interaction with AP-2 and subsequent internalization. These results suggest the surface expression of KIAA0319 is regulated by endocytosis, supporting the idea that the internalization and recycling of the protein may be involved in fine tuning its role in neuronal migration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural analysis of the interaction between Dishevelled2 and clathrin AP-2 adaptor, a critical step in noncanonical Wnt signaling.Structure. 2010 Oct 13;18(10):1311-20. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.07.010. Structure. 2010. PMID: 20947020 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of interaction sites on the N-terminal domain of clathrin heavy chain.Traffic. 2012 Jan;13(1):70-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01289.x. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Traffic. 2012. PMID: 21939487 Free PMC article.
-
Stonin 2 is an AP-2-dependent endocytic sorting adaptor for synaptotagmin internalization and recycling.Dev Cell. 2006 Feb;10(2):233-44. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.12.011. Dev Cell. 2006. PMID: 16459302
-
Cargo recognition during clathrin-mediated endocytosis: a team effort.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;16(4):392-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2004.06.001. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15261671 Review.
-
Sorting it out: AP-2 and alternate clathrin adaptors in endocytic cargo selection.J Cell Biol. 2003 Oct 27;163(2):203-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200309175. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14581447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Position of neocortical neurons transfected at different gestational ages with shRNA targeted against candidate dyslexia susceptibility genes.PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e65179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065179. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724130 Free PMC article.
-
Variants in the DYX2 locus are associated with altered brain activation in reading-related brain regions in subjects with reading disability.Neuroimage. 2012 Oct 15;63(1):148-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.037. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22750057 Free PMC article.
-
AU040320 deficiency leads to disruption of acrosome biogenesis and infertility in homozygous mutant mice.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 10;8(1):10379. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28666-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29991750 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout Mice for Dyslexia Susceptibility Gene Homologs KIAA0319 and KIAA0319L have Unaffected Neuronal Migration but Display Abnormal Auditory Processing.Cereb Cortex. 2017 Dec 1;27(12):5831-5845. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx269. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 29045729 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslexia associated gene KIAA0319 regulates cell cycle during human neuroepithelial cell development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 9;10:967147. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.967147. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36016658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar RC, Ohno H, Roche KW, Bonifacino JS. Functional domain mapping of the clathrin-associated adaptor medium chains mu1 and mu2. J Biol Chem 272: 27160–27166, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Anthoni H, Zucchelli M, Matsson H, Muller-Myhsok B, Fransson I, Schumacher J, Massinen S, Onkamo P, Warnke A, Griesemann H, Hoffmann P, Nopola-Hemmi J, Lyytinen H, Schulte-Korne G, Kere J, Nothen MM, and Peyrard-Janvid M. A locus on 2p12 containing the co-regulated MRPL19 and C2ORF3 genes is associated to dyslexia. Hum Mol Genet 16: 667–677, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Benmerah A, Lamaze C. Clathrin-coated pits: vive la difference? Traffic 8: 970–982, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino JS, Traub LM. Signals for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes. Annu Rev Biochem 72: 395–447, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

