ATF6alpha induces XBP1-independent expansion of the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 19420237
- PMCID: PMC2680102
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.045625
ATF6alpha induces XBP1-independent expansion of the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
A link exists between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) biogenesis and the unfolded protein response (UPR), a complex set of signaling mechanisms triggered by increased demands on the protein folding capacity of the ER. The UPR transcriptional activator X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) regulates the expression of proteins that function throughout the secretory pathway and is necessary for development of an expansive ER network. We previously demonstrated that overexpression of XBP1(S), the active form of XBP1 generated by UPR-mediated splicing of Xbp1 mRNA, augments the activity of the cytidine diphosphocholine (CDP-choline) pathway for biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) and induces ER biogenesis. Another UPR transcriptional activator, activating transcription factor 6alpha (ATF6alpha), primarily regulates expression of ER resident proteins involved in the maturation and degradation of ER client proteins. Here, we demonstrate that enforced expression of a constitutively active form of ATF6alpha drives ER expansion and can do so in the absence of XBP1(S). Overexpression of active ATF6alpha induces PtdCho biosynthesis and modulates the CDP-choline pathway differently than does enforced expression of XBP1(S). These data indicate that ATF6alpha and XBP1(S) have the ability to regulate lipid biosynthesis and ER expansion by mechanisms that are at least partially distinct. These studies reveal further complexity in the potential relationships between UPR pathways, lipid production and ER biogenesis.
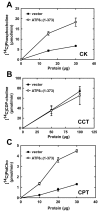
Figures







References
-
- Adachi, Y., Yamamoto, K., Okada, T., Yoshida, H., Harada, A. and Mori, K. (2008). ATF6 is a transcription factor specializing in the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Struct. Funct. 33, 75-89. - PubMed
-
- Back, S. H., Lee, K., Vink, E. and Kaufman, R. J. (2006). Cytoplasmic IRE1alpha-mediated XBP1 mRNA splicing in the absence of nuclear processing and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 18691-18706. - PubMed
-
- Calfon, M., Zeng, H., Urano, F., Till, J. H., Hubbard, S. R., Harding, H. P., Clark, S. G. and Ron, D. (2002). IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415, 92-96. - PubMed
-
- Fagone, P., Sriburi, R., Ward-Chapman, C., Frank, M., Wang, J., Gunter, C., Brewer, J. W. and Jackowski, S. (2007). Phospholipid biosynthesis program underlying membrane expansion during B-lymphocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7591-7605. - PubMed
-
- Gass, J. N., Gifford, N. M. and Brewer, J. W. (2002). Activation of an unfolded protein response during differentiation of antibody-secreting B cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49047-49054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

