Massage accelerates brain development and the maturation of visual function
- PMID: 19420271
- PMCID: PMC6665233
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5548-08.2009
Massage accelerates brain development and the maturation of visual function
Abstract
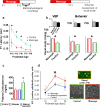
Environmental enrichment (EE) was shown recently to accelerate brain development in rodents. Increased levels of maternal care, and particularly tactile stimulation through licking and grooming, may represent a key component in the early phases of EE. We hypothesized that enriching the environment in terms of body massage may thus accelerate brain development in infants. We explored the effects of body massage in preterm infants and found that massage accelerates the maturation of electroencephalographic activity and of visual function, in particular visual acuity. In massaged infants, we found higher levels of blood IGF-1. Massage accelerated the maturation of visual function also in rat pups and increased the level of IGF-1 in the cortex. Antagonizing IGF-1 action by means of systemic injections of the IGF-1 antagonist JB1 blocked the effects of massage in rat pups. These results demonstrate that massage has an influence on brain development and in particular on visual development and suggest that its effects are mediated by specific endogenous factors such as IGF-1.
Figures

References
-
- Als H, Lawhon G, Duffy FH, McAnulty GB, Gibes-Grossman R, Blickman JG. Individualized developmental care for the very low-birth-weight preterm infant: medical and neurofunctional effects. JAMA. 1994;272:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Biagioni E, Bartalena L, Boldrini A, Cioni G, Giancola S, Ipata AE. Background EEG activity in preterm infants: correlation of outcome with selected maturational features. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1994;91:154–162. - PubMed
-
- Biagioni E, Bartalena L, Biver P, Pieri R, Cioni G. Electroencephalographic dysmaturity in preterm infants: a prognostic tool in the early postnatal period. Neuropediatrics. 1996;27:311–316. - PubMed
-
- Burton CL, Chatterjee D, Chatterjee-Chakraborty M, Lovic V, Grella SL, Steiner M, Fleming AS. Prenatal restraint stress and motherless rearing disrupts expression of plasticity markers and stress-induced corticosterone release in adult female Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Res. 2007;1158:28–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
