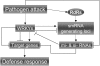
The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity
- PMID: 19420325
- PMCID: PMC2719123
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.138990
The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity
Figures
References
-
- Bostock RM (2005) Signal crosstalk and induced resistance: straddling the line between cost and benefit. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43 545–580 - PubMed
-
- Cai M, Qiu D, Yuan T, Ding X, Li H, Duan L, Xu C, Li X, Wang S (2008) Identification of novel pathogen-responsive cis-elements and their binding proteins in the promoter of OsWRKY13, a gene regulating rice disease resistance. Plant Cell Environ 31 86–96 - PubMed
-
- Caplan J, Padmanabhan M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2008) Plant NB-LRR immune receptors: from recognition to transcriptional reprogramming. Cell Host Microbe 3 126–135 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources