Myosin-interacting guanine exchange factor (MyoGEF) regulates the invasion activity of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through activation of RhoA and RhoC
- PMID: 19421144
- PMCID: PMC2692373
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.96
Myosin-interacting guanine exchange factor (MyoGEF) regulates the invasion activity of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through activation of RhoA and RhoC
Abstract
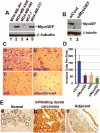
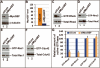
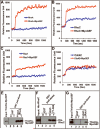
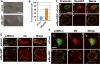
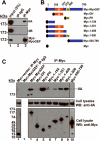
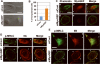
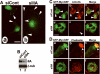
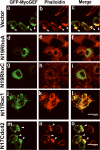
The small guanine triphosphatase (GTPase) proteins RhoA and RhoC are essential for tumor invasion and/or metastasis in breast carcinomas. However, it is poorly understood how RhoA and RhoC are activated in breast cancer cells. Here we describe the role of myosin-interacting guanine nucleotide exchange factor (Myo-GEF) in regulating RhoA and RhoC activation as well as cell polarity and invasion in an invasive breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. RNA-interference (RNAi)-mediated depletion of MyoGEF in MDA-MB-231 cells not only suppresses the activation of RhoA and RhoC, but also decreases cell polarity and invasion activity. The dominant-negative mutants of RhoA and RhoC, but not Rac1 and Cdc42, dramatically decrease actin polymerization induced by MyoGEF. In addition, MyoGEF co-localizes with nonmuscle myosin IIA (NMIIA) to the front of migrating cells, and depletion of NMIIA by RNAi disrupts the polarized localization of MyoGEF at the cell leading edge, suggesting a role for NMIIA in regulating MyoGEF localization and function. Moreover, MyoGEFprotein levels significantly increase in infiltrating ductal carcinomas as well as in invasive breast cancer cell lines. Taken together, our results suggest that MyoGEF cooperates with NMIIA to regulate the polarity and invasion activity of breast cancer cells through activation of RhoA and RhoC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intramolecular interactions between the Dbl homology (DH) domain and the carboxyl-terminal region of myosin II-interacting guanine nucleotide exchange factor (MyoGEF) act as an autoinhibitory mechanism for the regulation of MyoGEF functions.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):34033-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.607267. Epub 2014 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25336641 Free PMC article.
-
Rho isoform-specific interaction with IQGAP1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 2;287(45):38367-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.377499. Epub 2012 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22992742 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA and RhoC have distinct roles in migration and invasion by acting through different targets.J Cell Biol. 2011 May 16;193(4):655-65. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201011038. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21576392 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA, RhoB and RhoC have different roles in cancer cell migration.J Microsc. 2013 Sep;251(3):242-9. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12025. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Microsc. 2013. PMID: 23488932 Review.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1: a Janus-faced molecule in cellular signaling.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):483-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.034. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24308970 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction promotes microRNA signaling and RhoGTPase activation leading to tumor progression.Small GTPases. 2012 Jan-Mar;3(1):53-9. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.19110. Small GTPases. 2012. PMID: 22714418 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian Actin-binding Protein-1/Hip-55 Interacts with FHL2 and Negatively Regulates Cell Invasion.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jul 1;291(27):13987-13998. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.725739. Epub 2016 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129278 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RhoC in cancer cell migration.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Oct 9;21(1):527. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02234-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34627249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of the Small Rho GTPase Regulators-Complexities and Opportunities in Targeting Cancer Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 28;12(5):1092. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051092. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32353968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abl Kinases Regulate HGF/Met Signaling Required for Epithelial Cell Scattering, Tubulogenesis and Motility.PLoS One. 2015 May 6;10(5):e0124960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124960. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25946048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K, Rossman KL, Liu B, Ritola KD, Chiang D, Campbell SL, et al. Vav2 is an activator of Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10141–9. - PubMed
-
- Ahram M, Sameni M, Qiu RG, Linebaugh B, Kirn D, Sloane BF. Rac1-induced endocytosis is associated with intracellular proteolysis during migration through a three-dimensional matrix. Exp Cell Res. 2000;260:292–303. - PubMed
-
- Arthur WT, Ellerbroek SM, Der CJ, Burridge K, Wennerberg K. XPLN, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RhoA and RhoB, but not RhoC. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:42964–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

