Targeting murine heart and brain: visualisation conditions for multi-pinhole SPECT with (99m)Tc- and (123)I-labelled probes
- PMID: 19421750
- PMCID: PMC2724637
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-009-1142-9
Targeting murine heart and brain: visualisation conditions for multi-pinhole SPECT with (99m)Tc- and (123)I-labelled probes
Abstract
Purpose: The study serves to optimise conditions for multi-pinhole SPECT small animal imaging of (123)I- and (99m)Tc-labelled radiopharmaceuticals with different distributions in murine heart and brain and to investigate detection and dose range thresholds for verification of differences in tracer uptake.
Methods: A Triad 88/Trionix system with three 6-pinhole collimators was used for investigation of dose requirements for imaging of the dopamine D(2) receptor ligand [(123)I]IBZM and the cerebral perfusion tracer [(99m)Tc]HMPAO (1.2-0.4 MBq/g body weight) in healthy mice. The fatty acid [(123)I]IPPA (0.94 +/- 0.05 MBq/g body weight) and the perfusion tracer [(99m)Tc]sestamibi (3.8 +/- 0.45 MBq/g body weight) were applied to cardiomyopathic mice overexpressing the prostaglandin EP(3) receptor.
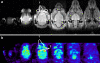
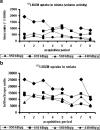
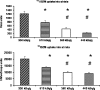
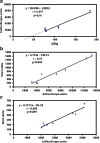
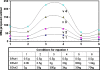
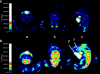
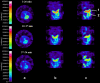
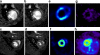
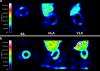
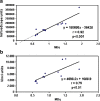
Results: In vivo imaging and in vitro data revealed 45 kBq total cerebral uptake and 201 kBq cardiac uptake as thresholds for visualisation of striatal [(123)I]IBZM and of cardiac [(99m)Tc]sestamibi using 100 and 150 s acquisition time, respectively. Alterations of maximal cerebral uptake of [(123)I]IBZM by >20% (116 kBq) were verified with the prerequisite of 50% striatal of total uptake. The labelling with [(99m)Tc]sestamibi revealed a 30% lower uptake in cardiomyopathic hearts compared to wild types. [(123)I]IPPA uptake could be visualised at activity doses of 0.8 MBq/g body weight.
Conclusion: Multi-pinhole SPECT enables detection of alterations of the cerebral uptake of (123)I- and (99m)Tc-labelled tracers in an appropriate dose range in murine models targeting physiological processes in brain and heart. The thresholds of detection for differences in the tracer uptake determined under the conditions of our experiments well reflect distinctions in molar activity and uptake characteristics of the tracers.
Figures
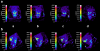

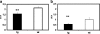
Similar articles
-
Challenge by the murine brain: multi-pinhole SPECT of 123I-labelled pharmaceuticals.J Neurosci Methods. 2008 Mar 15;168(2):282-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.10.011. Epub 2007 Oct 25. J Neurosci Methods. 2008. PMID: 18061274
-
Technetium-99m-labelled HL91 and technetium-99m-labelled MIBI SPECT imaging for the detection of ischaemic viable myocardium: a preliminary study.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2012 Jan;32(1):25-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097X.2011.01050.x. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22152075
-
Simultaneous acquisition of (99m)Tc- and (123)I-labeled radiotracers using a preclinical SPECT scanner with CZT detectors.Ann Nucl Med. 2016 May;30(4):263-71. doi: 10.1007/s12149-015-1055-6. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Ann Nucl Med. 2016. PMID: 26747655
-
Experimental studies of the physiologic properties of technetium-99m agents: myocardial transport of perfusion imaging agents.Am J Cardiol. 1990 Oct 16;66(13):9E-15E. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90606-2. Am J Cardiol. 1990. PMID: 2145753 Review.
-
Technetium-99m Radiopharmaceuticals for Ideal Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Lost and Found Opportunities.Molecules. 2022 Feb 10;27(4):1188. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041188. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35208982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1007/s00259-002-0805-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-002-0805-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12111135', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12111135/'}]}
- Beekman FJ, McElroy DP, Berger F, Gambhir SS, Hoffman EJ, Cherry SR. Towards in vivo nuclear microscopy: iodine-125 imaging in mice using micro-pinholes. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:933–8. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1109/TNS.2003.812437', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1109/tns.2003.812437'}]}
- Schramm NU, Ebel G, Engeland U, Schurrat T, Béhé M, Behr TM. High-resolution SPECT using multipinhole collimation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 2003;50:315–20.
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00716-2', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00716-2'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12906991', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12906991/'}]}
- Wu MC, Gao DW, Sievers RE, Lee RJ, Hasegawa BH, Dae MW. Pinhole single-photon emission computed tomography for myocardial perfusion imaging of mice. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42:576–82. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1109/TMI.2005.843782', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2005.843782'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16011315', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16011315/'}]}
- Goertzen AL, Jones DW, Seidel J, Li K, Green MV. First results from the high-resolution mouseSPECT annular scintillation camera. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2005;24:863–7. - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/art.21732', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21732'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16572444', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16572444/'}]}
- Ostendorf B, Scherer A, Wirrwar A, Hoppin JW, Lackas C, Schramm NU, et al. High-resolution multipinhole single-photon-emission computed tomography in experimental and human arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:1096–104. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

