Temporal expression of alternatively spliced forms of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in mice
- PMID: 19422457
- PMCID: PMC2776060
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03454.x
Temporal expression of alternatively spliced forms of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in mice
Abstract
Background: Mouse tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) is produced in three alternatively spliced isoforms that differ in domain structure and mechanism for cell surface binding. Tissue expression of TFPI isoforms in mice was characterized as an initial step for identification of their physiological functions.
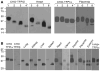
Methods and results: Sequence homology demonstrates that TFPIalpha existed over 430 Ma while TFPIbeta and TFPIgamma evolved more recently. In situ hybridization studies of heart and lung did not reveal any cells exclusively expressing a single isoform. Although our previous studies have demonstrated that TFPIalpha mRNA is more prevalent than TFPIbeta or TFPIgamma mRNA in mouse tissues, western blot studies demonstrated that TFPIbeta is the primary protein isoform produced in adult tissues, while TFPIalpha is expressed during embryonic development and in placenta. Consistent with TFPIbeta as the primary isoform produced within adult vascular beds, the TFPI isoform in mouse plasma migrates like TFPIbeta in SDS-PAGE and mice have a much smaller heparin-releasable pool of plasma TFPIalpha than humans.
Conclusions: The data demonstrate that alternatively spliced isoforms of TFPI are temporally expressed in mouse tissues at the level of protein production. TFPIalpha and TFPIbeta are produced in embryonic tissues and in placenta while adult tissues produce almost exclusively TFPIbeta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-gamma is an active alternatively spliced form of tissue factor pathway inhibitor present in mice but not in humans.J Thromb Haemost. 2008 Aug;6(8):1344-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03033.x. Epub 2008 May 22. J Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18503630 Free PMC article.
-
TFPIα and TFPIβ are expressed at the surface of breast cancer cells and inhibit TF-FVIIa activity.J Hematol Oncol. 2013 Jan 15;6:5. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23320987 Free PMC article.
-
Alternatively spliced isoforms of tissue factor pathway inhibitor.Thromb Res. 2010 Apr;125 Suppl 1:S52-6. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2010.01.038. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Thromb Res. 2010. PMID: 20176395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the inhibitory activities of human tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI)α and TFPIβ.J Thromb Haemost. 2013 May;11(5):911-8. doi: 10.1111/jth.12188. J Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23480518 Free PMC article.
-
Biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor.Blood. 2014 May 8;123(19):2934-43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-512764. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24620349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activated protein C up-regulates procoagulant tissue factor activity on endothelial cells by shedding the TFPI Kunitz 1 domain.Blood. 2011 Jun 9;117(23):6338-46. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-316257. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21474669 Free PMC article.
-
TFPIα anticoagulant function is highly dependent on protein S in vivo.Sci Adv. 2024 Feb 2;10(5):eadk5836. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk5836. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38306422 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of coagulation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor: Implications for hemophilia therapy.J Thromb Haemost. 2022 Jun;20(6):1290-1300. doi: 10.1111/jth.15697. Epub 2022 Mar 27. J Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35279938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitors as Potential Targets for Understanding the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 22;11(5):1237. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051237. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Jun;13 Suppl 1(0 1):S200-7. doi: 10.1111/jth.12897. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 26149025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Panes O, Matus V, Saez CG, Quiroga T, Pereira J, Mezzano D. Human platelets synthesize and express functional tissue factor. Blood. 2007;109:5242–50. - PubMed
-
- Mackman N, Tilley RE, Key NS. Role of the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation in hemostasis and thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:1687–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

