Early angiography in patients with chronic kidney disease: a collaborative systematic review
- PMID: 19423566
- PMCID: PMC2689886
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05551008
Early angiography in patients with chronic kidney disease: a collaborative systematic review
Abstract
Background and objectives: In the general population, an early invasive strategy of routine coronary angiography is superior to a conservative strategy of selective angiography in patients who are admitted with unstable angina or non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI), but the effectiveness of this strategy in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is uncertain.
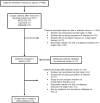
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We conducted a collaborative meta-analysis with data provided by the main authors of identified trials to estimate the effectiveness of early angiography in patients with CKD. The Cochrane, Medline, and EMBASE databases were searched to identify randomized trials that compared invasive and conservative strategies in patients with unstable angina or non-ST MI. Pooled risks ratios were estimated using data from enrolled patients with estimated GFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2).
Results: Five randomized trials that enrolled 1453 patients with CKD were included. An early invasive strategy was associated with nonsignificant reductions in all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, and a composite of death or nonfatal MI. The invasive strategy significantly reduced rehospitalization.
Conclusions: This collaborative study suggests that the benefits of an early invasive strategy are preserved in patients with CKD and that an early invasive approach reduces the risk for rehospitalization and is associated with trends of reduction in the risk for death and nonfatal re-infarction in patients with CKD. Coronary angiography should be considered for patients who have CKD and are admitted with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes.
Figures

References
-
- Choudhry NK, Singh JM, Barolet A, Tomlinson GA, Detsky AS: How should patients with unstable angina and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction be managed? A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Med 118: 465–474, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Mehta SR, Cannon CP, Fox KA, Wallentin L, Boden WE, Spacek R, Widimsky P, McCullough PA, Hunt D, Braunwald E, Yusuf S: Routine vs selective invasive strategies in patients with acute coronary syndromes: A collaborative meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA 293: 2908–2917, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, Bridges CR, Califf RM, Casey DE Jr, Chavey WE 2nd, Fesmire FM, Hochman JS, Levin TN, Lincoff AM, Peterson ED, Theroux P, Wenger NK, Wright RS, Smith SC Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Halperin JL, Hunt SA, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lytle BW, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B: ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) developed in collaboration with the American College of Emergency Physicians, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation and the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol 50: e1–e157, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Murphy SW: Management of heart failure and coronary artery disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Semin Dial 16: 165–172, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 41: 1–12, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

