Interleukin-17A is not expressed by CD207(+) cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis lesions
- PMID: 19424201
- PMCID: PMC2820828
- DOI: 10.1038/nm0509-483
Interleukin-17A is not expressed by CD207(+) cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis lesions
Abstract
Interleukin-17 (IL-17A) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that has recently been implicated in pathogenesis of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH), a potentially fatal disease characterized by lesions including CD207+ (langerin +) histiocytes. However, in this study we were unable to identify IL-17A gene expression in Langerhans cell lesions, and plasma levels of IL-17A did not correlate with disease activity. Therefore, this study does not support a central role for IL-17A in LCH pathogenesis.
Figures

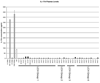
Comment on
-
Langerhans cell histiocytosis reveals a new IL-17A-dependent pathway of dendritic cell fusion.Nat Med. 2008 Jan;14(1):81-7. doi: 10.1038/nm1694. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18157139
References
-
- Arceci RJ. The histiocytoses: the fall of the Tower of Babel. Eur. J. Cancer. 1999;35:747–767. - PubMed
-
- McClain KL, Natkunam Y, Swerdlow SH. Atypical cellular disorders. Hematology. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2004:283–296. - PubMed
-
- Coury F, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis reveals a new IL-17Adependent pathway of dendritic cell fusion. Nat. Med. 2008;14:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Dong C. TH17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008;8:337–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

