Multiphoton microscopy of prostate and periprostatic neural tissue: a promising imaging technique for improving nerve-sparing prostatectomy
- PMID: 19425823
- PMCID: PMC2841021
- DOI: 10.1089/end.2009.0221
Multiphoton microscopy of prostate and periprostatic neural tissue: a promising imaging technique for improving nerve-sparing prostatectomy
Abstract
Background and purpose: Various imaging modalities are under investigation for real-time tissue imaging of periprostatic nerves with the idea of improving the results of nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. We explored multiphoton microscopy (MPM) for real-time tissue imaging of the prostate and periprostatic neural tissue in a male Sprague-Dawley rat model. The unique advantage of this technique is the acquisition of high-resolution images without necessitating any extrinsic labeling agent and with minimal phototoxic effect on tissue.
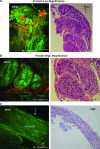
Materials and methods: The prostate and cavernous nerves were surgically excised from male Sprague-Dawley rats. The imaging was carried out using intrinsic fluorescence and scattering properties of the tissues without any exogenous dye or contrast agent. A custom-built MPM, consisting of an Olympus BX61WI upright frame and a modified MRC 1024 scanhead, was used. A femtosecond pulsed titanium/sapphire laser at 780-nm wavelength was used to excite the tissue; laser power under the objective was modulated via a Pockels cell. Second harmonic generation (SHG) signals were collected at 390 (+/-35 nm), and broadband autofluorescence was collected at 380 to 530 nm. The images obtained from SHG and from tissue fluorescence were then merged and color coded during postprocessing for better appreciation of details. The corresponding tissues were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin staining for histologic confirmation of the structures.
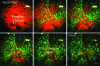
Results: High-resolution images of the prostate capsule, underlying acini, and individual cells outlining the glands were obtained at varying magnifications. MPM images of adipose tissue and the neural tissues were also obtained. Histologic confirmation and correlation of the prostate gland, fat, cavernous nerve, and major pelvic ganglion validated the findings of MPM.
Conclusion: Real-time imaging and microscopic resolution of prostate and periprostatic neural tissue using MPM is feasible without the need for any extrinsic labeling agents. Integration of this imaging modality with operative technique has the potential to improve the precision of nerve-sparing prostatectomy.
Figures





References
-
- Murphy GP. Mettlin C. Menck H. Winchester DP. Davidson AM. National patterns of prostate cancer treatment by radical prostatectomy: Results of a survey by the American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer. J Urol. 1994;152:1817–1819. - PubMed
-
- Talcott JA. Rieker P. Propert KJ. Clark JA. Wishnow KI. Loughlin KR. Richie JP. Kantoff PW. Patient-reported impotence and incontinence after nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997;89:1117–1123. - PubMed
-
- Weldon VE. Tavel FR. Neuwirth H. Continence, potency and morbidity after radical perineal prostatectomy. J Urol. 1997;158:1470–1475. - PubMed
-
- Catalona WJ. Carvalhal GF. Mager DE. Smith DS. Potency, continence and complication rates in 1,870 consecutive radical retropubic prostatectomies. J Urol. 1999;162:433–438. - PubMed
-
- Walsh PC. Marschke P. Ricker D. Burnett AL. Patient-reported urinary continence and sexual function after anatomic radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2000;55:58–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

