PD-1 signaling in primary T cells
- PMID: 19426218
- PMCID: PMC3424066
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00767.x
PD-1 signaling in primary T cells
Abstract
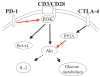
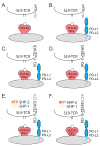
Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a cell surface molecule that regulates the adaptive immune response. Engagement of PD-1 by its ligands PD-L1 or PD-L2 transduces a signal that inhibits T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and cytolytic function. While a great deal is known concerning the biologic roles PD-1 plays in regulating the primary immune response and in T-cell exhaustion, comparatively little is known regarding how PD-1 ligation alters signaling pathways. PD-1 ligation is known to inhibit membrane-proximal T-cell signaling events, while ligation of the related inhibitory molecule cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 appears to target more downstream signaling pathways. A major obstacle to an in-depth understanding of PD-1 signaling is the lack of physiologic models in which to study signal transduction. This review focuses on: (i) signaling pathways altered by PD-1 ligation, (ii) factors recruited upon PD-1 phosphorylation, and (iii) exploring the hypothesis that PD-1 ligation induces distinct signals during various stages of immune-cell differentiation. Lastly, we describe models to dissect the function of the PD-1 cytoplasmic tail using primary cells in the absence of agonist antibodies.
Figures

References
-
- Okazaki T, Honjo T. The PD-1-PD-L pathway in immunological tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Wherry EJ, Ha SJ, Kaech SM, Haining WN, Sarkar S, Kalia V, Subramaniam S, Blattman JN, Barber DL, Ahmed R. Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity. 2007;27:670–684. - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Wherry EJ, Masopust D, Zhu B, Allison JP, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ, Ahmed R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature. 2006;439:682–687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

