Does readiness to change predict subsequent alcohol consumption in medical inpatients with unhealthy alcohol use?
- PMID: 19428189
- PMCID: PMC2789443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2009.03.034
Does readiness to change predict subsequent alcohol consumption in medical inpatients with unhealthy alcohol use?
Abstract
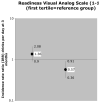
We studied whether readiness to change predicts alcohol consumption (drinks per day) 3 months later in 267 medical inpatients with unhealthy alcohol use. We used 3 readiness to change measures: a 1 to 10 visual analog scale (VAS) and two factors of the Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale: Perception of Problems (PP) and Taking Action (TA). Subjects with the highest level of VAS-measured readiness consumed significantly fewer drinks 3 months later [Incidence rate ratio (IRR) and 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.57 (0.36, 0.91) highest vs. lowest tertile]. Greater PP was associated with more drinking [IRR (95%CI): 1.94 (1.02, 3.68) third vs. lowest quartile]. Greater TA scores were associated with less drinking [IRR (95%CI): 0.42 (0.23, 0.78) highest vs. lowest quartile]. Perception of Problems' association with more drinking may reflect severity rather than an aspect of readiness associated with ability to change; high levels of Taking Action appear to predict less drinking. Although assessing readiness to change may have clinical utility, assessing the patient's planned actions may have more predictive value for future improvement in alcohol consumption.
Figures

References
-
- Amrhein PC, Miller WR, Yahne CE, Palmer M, Fulcher L. Client commitment language during motivational interviewing predicts drug use outcomes. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2003;71(5):862–878. - PubMed
-
- Bertholet N, Daeppen JB, Wietlisbach V, Fleming M, Burnand B. Reduction of alcohol consumption by brief alcohol intervention in primary care: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(9):986–995. - PubMed
-
- Demmel R, Beck B, Richter D, Reker T. Readiness to change in a clinical sample of problem drinkers: relation to alcohol use, self-efficacy, and treatment outcome. Eur Addict Res. 2004;10(3):133–138. - PubMed
-
- Figlie NB, Dunn J, Laranjeira R. Factor structure of the Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES) in alcohol dependent outpatients. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2004;26(2):91–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

