Signal intensities of radiolabeled cRNA probes used alone or in combination with non-isotopic in situ hybridization histochemistry
- PMID: 19428522
- PMCID: PMC2700003
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.01.022
Signal intensities of radiolabeled cRNA probes used alone or in combination with non-isotopic in situ hybridization histochemistry
Abstract
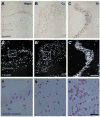
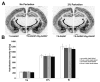
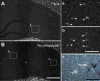
This study addressed the question of whether radioactive hybridization signal intensities are reduced in combined isotopic and non-isotopic double in situ hybridization (DISH) compared with those in single in situ hybridization (ISH). Non-isotopic digoxigenin (Dig)-labeled hybrids were detected using an alkaline phosphatase (AP) enzymatic reaction which results in nitroblue tetrazolium chloride (NBT)/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (BCIP)-salt precipitation that could shield S35-radiation from penetrating to the surface. Sections were plastic coated of with 2% parlodion to prevent a chemical reaction between AP and developer during processing of the photosensitive emulsion, which could further reduce radioactive hybridization signal detection by autoradiography. We used DISH with a hybridization cocktail of radioactive S35- and Dig-labeled GAD67 cRNA probes. In order to avoid competition for the same complementary sequence, the probes were directed towards different sequences of the glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67) mRNA, resulting in co-detection of isotopic and non-isotopic hybrids in close to 100% of GAD67 positive cells. Quantitation of autoradiograms showed that there was no reduction of autoradiographic signal intensity from S35-labeled hybrids in the presence of Dig-labeled hybrids. Plastic coating of single or dual hybridized sections did not reduce the radioactive signal intensity. When mRNAs for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunits were detected with subunit specific S35-labeled cRNA probes in GAD67 hippocampal interneurons the total numbers of nAChR subunit expressing cells remained the same in single or double hybridized sections even for low abundant mRNAs. Together, these results indicate that combined radioactive and non-radioactive DISH does not interfere with the detection of the radiation signal from the S35-labeled hybrids, and neither specificity nor sensitivity is compromised.
Figures
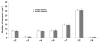
Similar articles
-
Expression of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit mRNAs in rat hippocampal GABAergic interneurons.J Comp Neurol. 2008 Nov 10;511(2):286-99. doi: 10.1002/cne.21828. J Comp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18792073 Free PMC article.
-
A method for simultaneous detection of multiple mRNAs using digoxigenin and radioisotopic cRNA probes.J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Dec;41(12):1741-50. doi: 10.1177/41.12.8245421. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993. PMID: 8245421
-
Simultaneous isotopic and nonisotopic in situ hybridization histochemistry with cRNA probes.Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 1998 Sep;3(1):22-32. doi: 10.1016/s1385-299x(98)00017-8. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 1998. PMID: 9767088
-
In situ hybridization using cRNA probes: isotopic and nonisotopic detection methods.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;326:17-31. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-007-3:17. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16780192 Review.
-
Detection of mRNAs encoding peroxisomal proteins by non-radioactive in situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labelled cRNAs.Histochem Cell Biol. 1997 Oct-Nov;108(4-5):371-9. doi: 10.1007/s004180050178. Histochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9387930 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuregulin and dopamine modulation of hippocampal gamma oscillations is dependent on dopamine D4 receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Aug 7;109(32):13118-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201011109. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22822214 Free PMC article.
-
Double and triple in situ hybridization for coexpression studies: combined fluorescent and chromogenic detection of neuropeptide Y (NPY) and serotonin receptor subtype mRNAs expressed at different abundance levels.Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;137(1):11-24. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0882-3. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22075564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azam L, Winzer-Serhan U, Leslie FM. Co-expression of alpha7 and beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit mRNAs within rat brain cholinergic neurons. Neuroscience. 2003;119:965–77. - PubMed
-
- Bizon JL, Lauterborn JC, Gall CM. Subpopulations of striatal interneurons can be distinguished on the basis of neurotrophic factor expression. J Comp Neurol. 1999;408:283–98. - PubMed
-
- Chiu KP, Duca KA, Berman SA, Sullivan T, Bursztajn S. A novel in situ double-labeling method for simultaneous detection of mRNA and expressed protein or two different mRNAs. J Neurosci Methods. 1996;66:69–79. - PubMed
-
- Chotteau-Lelièvre A, Dollé P, Gofflot F. Expression analysis of murine genes using in situ hybridization with radioactive and nonradioactively labeled RNA probes. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;326:61–87. - PubMed
-
- Cox KH, DeLeon DV, Angerer LM, Angerer RC. Detection of mRNAs in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984;101:485–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

