Acquiring local field potential information from amperometric neurochemical recordings
- PMID: 19428527
- PMCID: PMC2708671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.01.023
Acquiring local field potential information from amperometric neurochemical recordings
Abstract
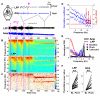
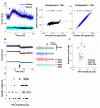
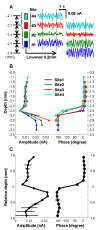
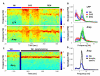
Simultaneous acquisition of in vivo electrophysiological and neurochemical information is essential for understanding how endogenous neurochemicals modulate the dynamics of brain activity. However, up to now such a task has rarely been accomplished due to the major technical challenge of operating two independent recording systems simultaneously in real-time. Here we propose a simpler solution for achieving this goal by using only a standard electrochemical technique--amperometry. To demonstrate its feasibility, we compared amperometric signals with simultaneously recorded local field potential (LFP) signals. We found that the high frequency component (HFC) of the amperometric signals did not reflect neurochemical fluctuations, but instead it resembled LFPs in several aspects, including: (1) coherent spectral fluctuations; (2) clear characterization of different brain states; (3) identical hippocampal theta depth profile. As such, our findings provide the first demonstration that both LFP and local neurochemical information can be simultaneously acquired from electrochemical sensors alone.
Figures
References
-
- Bland BH, Whishaw IQ. Generators and topography of hippocampal theta (RSA) in the anaesthetized and freely moving rat. Brain Res. 1976;118:259–80. - PubMed
-
- Burmeister JJ, Palmer M, Gerhardt GA. Ceramic-based multisite microelectrode array for rapid choline measures in brain tissue. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2003;481:65–74.
-
- Burmeister JJ, Pomerleau F, Huettl P, Gash CR, Werner CE, Bruno JP, Gerhardt GA. Ceramic-based multisite microelectrode arrays for simultaneous measures of choline and acetylcholine in CNS. Biosens Bioelectron. 2008;23:1382–9. - PubMed
-
- Chang Q, Savage LM, Gold PE. Microdialysis measures of functional increases in ACh release in the hippocampus with and without inclusion of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in the perfusate. J Neurochem. 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

