Female fear: influence of estrus cycle on behavioral response and neuronal activation
- PMID: 19428610
- PMCID: PMC2739660
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.01.019
Female fear: influence of estrus cycle on behavioral response and neuronal activation
Abstract
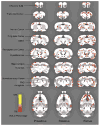
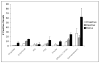
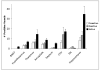
Our observation that male rat's innate fear response differed with hormonal status, as well as the higher prevalence of fear and anxiety disorders in human females led to the current investigation of the impact of phases of the estrus cycle on innate fear responding. Female rats in different phases of the cycle were exposed to an innate fear-inducing stimulus (2,5-dihydro-2,4,5-trimethylthiazoline, TMT odor) and monitored for changes in behavior and brain activation. Behavioral data showed freezing responses to TMT were significantly enhanced during estrus as compared to other phases of the cycle. This data was supported by significant increases in pixel intensity in cortical and sub-cortical regions in estrus compared to proestrus and diestrus. Imaging results demonstrated significant increases in brain activation in the somatosensory and insular cortices when comparing estrus to diestrus. There were significant increases in neural activity in the bed nucleus of the stria terminals (BNST) and septum in estrus as compared to proestrus. Additionally, the hippocampus, hypothalamus, olfactory system, and cingulate cortex show significant increases in the estrus phase when compared to both diestrus and proestrus. Taken together, these results suggest that the female's hormonal status may be correlated with alterations in both neuronal and behavioral indices of fear.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estrous cycle phase and gonadal hormones influence conditioned fear extinction.Neuroscience. 2009 Dec 15;164(3):887-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.09.011. Epub 2009 Sep 15. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19761818 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian steroids regulate neuropeptides in the trigeminal ganglion.Neuropeptides. 2005 Aug;39(4):409-17. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2005.04.002. Neuropeptides. 2005. PMID: 15936815
-
Estrogen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in female rat brain during the estrous cycle: a comparison with ovariectomized females and intact males.Endocrinology. 1992 Jul;131(1):381-8. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.1.1612018. Endocrinology. 1992. PMID: 1612018
-
The female gender protects against pulmonary injury after trauma hemorrhagic shock.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2001 Fall;2(3):231-40. doi: 10.1089/109629601317202713. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2001. PMID: 12593713
-
Influence of the estrous cycle on c-fos and CRH gene transcription in the brain of endotoxin-challenged female rats.Neuroendocrinology. 1997 Jan;65(1):29-46. doi: 10.1159/000127162. Neuroendocrinology. 1997. PMID: 9032772
Cited by
-
Empathic fear responses in mice are triggered by recognition of a shared experience.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 18;8(9):e74609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074609. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24058601 Free PMC article.
-
Functional MRI of the mouse olfactory system.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Jun 21;704:57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.03.055. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30951799 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neurogenesis mediates sex-specific effects of social isolation and exercise on fear extinction in adolescence.Neurobiol Stress. 2021 Jul 13;15:100367. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100367. eCollection 2021 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2021. PMID: 34337114 Free PMC article.
-
Brain processing of biologically relevant odors in the awake rat, as revealed by manganese-enhanced MRI.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048491. Epub 2012 Oct 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23119035 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Estrogen Influences Predator Odor-Induced Impairment of Cognitive and Social Behaviors in Aromatase Gene Deficiency Mice.Behav Neurol. 2021 Sep 20;2021:5346507. doi: 10.1155/2021/5346507. eCollection 2021. Behav Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34594430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoniadis EA, McDonald RJ. Amygdala, hippocampus and discriminative fear conditioning in context. Behav Brain Res. 2000;108:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DM, Yee BK, Lemaire M, Jarrard L, Iversen SD. Contextual fear conditioning is disrupted by lesions of the subcortical, but not entorhinal, connections to the hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 2001;141:304–311. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC, Rodgers J, Weiss SM. The characterization and modeling of antipredator defensive behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;40:819–28. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC. Effects of hippocampal lesions on the rat's reaction to a cat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1972;78:77–82. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard, Yang, Li, Gervacio, Blanchard Cue and context conditioning of defensive behaviors to cat odor stimuli. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2001;25:587–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

