Intradermal immunization improves protective efficacy of a novel TB vaccine candidate
- PMID: 19428920
- PMCID: PMC2743149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.03.018
Intradermal immunization improves protective efficacy of a novel TB vaccine candidate
Abstract
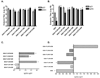
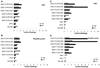
We have developed the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) fusion protein (ID83), which contains the three Mtb proteins Rv1813, Rv3620 and Rv2608. We evaluated the immunogenicity and protective efficacy of ID83 in combination with several emulsion-formulated toll-like receptor agonists. The ID83 subunit vaccines containing synthetic TLR4 or TLR9 agonists generated a T helper-1 immune response and protected mice against challenge with Mtb regardless of route. The ID83 vaccine formulated with gardiquimod (a TLR7 agonist) also resulted in a protective response when administered intradermally, whereas the same vaccine given subcutaneously failed to provide protection. This highlights the need to explore different routes of immunization based on the adjuvant formulations used.
Figures


References
-
- Dye C, Floyd F, Uplekar M. Global Tuberculosis Control: surveillance, planning, financing: WHO report: World Health Organization. 2008.
-
- Dye C, Watt CJ, Bleed DM, Hosseini SM, Raviglione MC. Evolution of tuberculosis control and prospects for reducing tuberculosis incidence, prevalence, and deaths globally. Jama. 2005 Jun 8;293(22):2767–2775. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Doherty TM. The success and failure of BCG - implications for a novel tuberculosis vaccine. Nature reviews. 2005 Aug;3(8):656–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

