Angiotensin II inhibits GABAergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray neurons
- PMID: 19429096
- PMCID: PMC2929652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.063
Angiotensin II inhibits GABAergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray neurons
Abstract
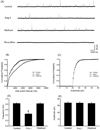
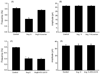
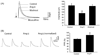
The purpose of this study was to determine the role of angiotensin II (Ang II) in modulating inhibitory and excitatory synaptic inputs to the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG). The whole cell voltage-clamp recording was performed to examine inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs and EPSCs) of the dl-PAG neurons. Ang II, at the concentration of 2microM, decreased the frequency of miniature IPSCs from 0.83+/-0.02 to 0.45+/-0.03Hz (P<0.05) in 10 tested neurons. This did not significantly affect the amplitude and decay time constant. The effect of Ang II on miniature IPSCs was blocked by the prior application of Ang II AT1 receptor antagonist losartan, but not by AT2 receptor antagonist PD123319. Additionally, Ang II decreased the amplitude of evoked IPSCs from 148+/-15 to 89+/-7pA (P<0.05), and increased the paired-pulse ratio from 96+/-5% to 125+/-7% (P<0.05) in eight tested neurons. In contrast, Ang II had no distinct effects on the EPSCs. Our data suggest that Ang II inhibits GABAergic synaptic inputs to the dl-PAG through activation of presynaptic AT1 receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II facilitates GABAergic neurotransmission at postsynaptic sites in rat amygdala neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2018 May 1;133:334-344. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29447844
-
Angiotensin II stimulates spinally projecting paraventricular neurons through presynaptic disinhibition.J Neurosci. 2003 Jun 15;23(12):5041-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-12-05041.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12832527 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic P2X receptors presynaptically increase glutamatergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray.Brain Res. 2008 May 7;1208:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.083. Epub 2008 Mar 8. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18395189 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic angiotensin II AT1 receptors enhance inhibitory and excitatory synaptic neurotransmission to motoneurons and other ventral horn neurons in neonatal rat spinal cord.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Aug;94(2):1405-12. doi: 10.1152/jn.00165.2005. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 16061493
-
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) inhibits glutamatergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray (dl-PAG).Brain Res. 2007 Aug 8;1162:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.004. Epub 2007 Jun 16. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17612511 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation and comparison of anticonvulsant activity of telmisartan and olmesartan in experimentally induced animal models of epilepsy.J Clin Diagn Res. 2014 Oct;8(10):HC08-11. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/9455.5061. Epub 2014 Oct 20. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014. PMID: 25478368 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-II Modulates GABAergic Neurotransmission in the Mouse Substantia Nigra.eNeuro. 2021 Apr 20;8(2):ENEURO.0090-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0090-21.2021. Print 2021 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 33771900 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II centrally induces frequent detrusor contractility of the bladder by acting on brain angiotensin II type 1 receptors in rats.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 24;6:22213. doi: 10.1038/srep22213. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26908391 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II, a stress-related neuropeptide in the CNS, facilitates micturition reflex in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;175(18):3727-3737. doi: 10.1111/bph.14439. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29981238 Free PMC article.
-
Role of angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas-R-nNOS pathways in amplified neuronal activity of dorsolateral periaqueductal gray after chronic heart failure.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Mar 20;563:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.01.025. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24472567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albin RL, Makowiec RL, Hollingsworth Z, Dure LS, Penney JB, Young AB. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the periaqueductal gray of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1990;118:112–115. - PubMed
-
- Bandler R, Carrive P, Zhang SP. Integration of somatic and autonomic reactions within the midbrain periaqueductal gray: viscerotopic, somatotopic and functional organization. Prog. Brain Res. 1991;87:269–305. - PubMed
-
- Beitz AJ, Williams FG. In: Localization of putative amino acid transmitters in the PAG and their relationship to the PAG–raphe magnus pathway. Depaulis A, Bandler R, editors. Plenum, NewYork: The Midbrain Periaqueductal Gray Matter; 1991.
-
- Bowery NG, Hudson AL, Price GW. GABAA and GABAB receptor site distribution in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1987;20:365–383. - PubMed
-
- Brooks VL. Interactions between angiotensin II and the sympathetic nervous system in the long-term control of arterial pressure. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1997;24:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

