Hyperglycemia-enhanced ischemic brain damage in mutant manganese SOD mice is associated with suppression of HIF-1alpha
- PMID: 19429140
- PMCID: PMC2680794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.076
Hyperglycemia-enhanced ischemic brain damage in mutant manganese SOD mice is associated with suppression of HIF-1alpha
Abstract
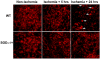
Both preischemic hyperglycemia and reduction of manganese superoxide dismutase activity are known to enhance neuronal death induced by transient cerebral ischemia. Transcriptional factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) regulates multiple downstream genes that modulate cell metabolism, survival, death, angiogenesis, hematopoiesis, and other functions. The objectives of this study were to determine (i) whether hyperglycemia is able to increase ischemic brain damage in mutant manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2) mice and (ii) whether the reduction of SOD2 activity has a profound effect on HIF-1 protein expression under hyperglycemic ischemic condition. Both wild type and mutant SOD deficient (SOD2(-/+)) mice were induced to hyperglycemia 30min before induction of a 30-min transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). Brains were extracted after 5 and 24h of reperfusion for immunohistochemistry and Western blot analyses. The results showed that preischemic hyperglycemia significantly increased infarct volume in SOD2(-/+)mice and that HIF-1alpha protein levels were significantly reduced in ischemic core area at 5- and 24-h of reperfusion in hyperglycemic SOD2(-/+) mice. However, the HIF-1alpha protein levels were not significantly decreased in hyperglycemic wild type animals subjected to stroke. The results suggest that the increased brain damage observed in hyperglycemic SOD2(-/+) mice is associated with HIF-1alpha suppression, while hyperglycemia per se does not seem to exert its detrimental effects on ischemic brain via modulating HIF-1 pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Agani FH, Pichiule P, Carlos Chavez J, LaManna JC. Inhibitors of mitochondrial complex I attenuate the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 during hypoxia in Hep3B cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2002;132:107–9. - PubMed
-
- Allen KL, Almeida A, Bates TE, Clark JB. Changes of respiratory chain activity in mitochondrial and synaptosomal fractions isolated from the gerbil brain after graded ischaemia. J Neurochem. 1995;64:2222–9. - PubMed
-
- Aminova LR, Chavez JC, Lee J, Ryu H, Kung A, Lamanna JC, Ratan RR. Prosurvival and prodeath effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha stabilization in a murine hippocampal cell line. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:3996–4003. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron M, Yu AY, Solway KE, Semenza GL, Sharp FR. Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) and its target genes following focal ischaemia in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:4159–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

