The function of non-coding RNAs in genomic imprinting
- PMID: 19429783
- PMCID: PMC2847617
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.030403
The function of non-coding RNAs in genomic imprinting
Abstract
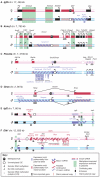
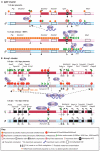
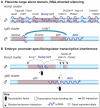
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that regulate gene expression in cis or in trans are a shared feature of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. In mammals, cis-acting functions are associated with macro ncRNAs, which can be several hundred thousand nucleotides long. Imprinted ncRNAs are well-studied macro ncRNAs that have cis-regulatory effects on multiple flanking genes. Recent advances indicate that they employ different downstream mechanisms to regulate gene expression in embryonic and placental tissues. A better understanding of these downstream mechanisms will help to improve our general understanding of the function of ncRNAs throughout the genome.
Figures

References
-
- Allis CD, Berger SL, Cote J, Dent S, Jenuwien T, Kouzarides T, Pillus L, Reinberg D, Shi Y, Shiekhattar R, et al. New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell. 2007a;131:633–636. - PubMed
-
- Allis CD, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D. Overview and concepts. In: Allis CD, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D, Caparros M, editors. Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2007b. pp. 23–61.
-
- Amaral PP, Mattick JS. Noncoding RNA in development. Mamm. Genome. 2008;19:454–492. - PubMed
-
- Barlow DP, Bartolomei MS. Genomic imprinting in mammals. In: Allis CD, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D, Caparros M, editors. Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2007. pp. 357–375.
-
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000;405:482–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

