Resveratrol induces mitochondrial biogenesis in endothelial cells
- PMID: 19429820
- PMCID: PMC2711732
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00368.2009
Resveratrol induces mitochondrial biogenesis in endothelial cells
Abstract
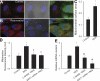
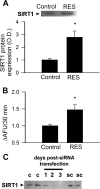
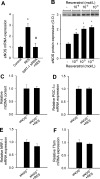
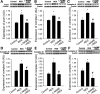
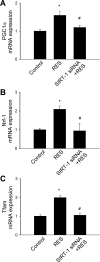
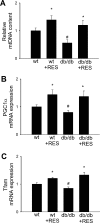
Pathways that regulate mitochondrial biogenesis are potential therapeutic targets for the amelioration of endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease. Resveratrol was shown to impact mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle and the liver, but its role in mitochondrial biogenesis in endothelial cells remains poorly defined. The present study determined whether resveratrol induces mitochondrial biogenesis in cultured human coronary arterial endothelial cells (CAECs). In CAECs resveratrol increased mitochondrial mass and mitochondrial DNA content, upregulated protein expression of electron transport chain constituents, and induced mitochondrial biogenesis factors (proliferator-activated receptor-coactivator-1alpha, nuclear respiratory factor-1, mitochondrial transcription factor A). Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) was induced, and endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS) was upregulated in a SIRT1-dependent manner. Knockdown of SIRT1 (small interfering RNA) or inhibition of NO synthesis prevented resveratrol-induced mitochondrial biogenesis. In aortas of type 2 diabetic (db/db) mice impaired mitochondrial biogenesis was normalized by chronic resveratrol treatment, showing the in vivo relevance of our findings. Resveratrol increases mitochondrial content in endothelial cells via activating SIRT1. We propose that SIRT1, via a pathway that involves the upregulation of eNOS, induces mitochondrial biogenesis. Resveratrol induced mitochondrial biogenesis in the aortas of type 2 diabetic mice, suggesting the potential for new treatment approaches targeting endothelial mitochondria in metabolic diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
A glass of red wine to improve mitochondrial biogenesis? Novel mechanisms of resveratrol.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):H8-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00471.2009. Epub 2009 May 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19465547 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barsoum MJ, Yuan H, Gerencser AA, Liot G, Kushnareva Y, Graber S, Kovacs I, Lee WD, Waggoner J, Cui J, White AD, Bossy B, Martinou JC, Youle RJ, Lipton SA, Ellisman MH, Perkins GA, Bossy-Wetzel E. Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial fission is regulated by dynamin-related GTPases in neurons. EMBO J 25: 3900–3911, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, Pistell PJ, Poosala S, Becker KG, Boss O, Gwinn D, Wang M, Ramaswamy S, Fishbein KW, Spencer RG, Lakatta EG, Le Couteur D, Shaw RJ, Navas P, Puigserver P, Ingram DK, de Cabo R, Sinclair DA. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444: 337–342, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baur JA, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nature Rev 5: 493–506, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

