Colocalization of prostaglandin F(2alpha) receptor FP and prostaglandin F synthase-I in the spinal cord
- PMID: 19429887
- PMCID: PMC2739758
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M800543-JLR200
Colocalization of prostaglandin F(2alpha) receptor FP and prostaglandin F synthase-I in the spinal cord
Abstract
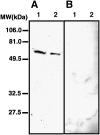
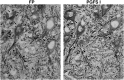
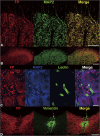
Prostaglandin F(2alpha) is synthesized by prostaglandin F synthase, which exists in two types, prostaglandin F synthase I (PGFS I) and prostaglandin F synthase II (PGFS II). Prostaglandin F(2alpha) binds to its specific receptor, FP. Our previous immunohistochemical study showed the distinct localization of prostaglandin F synthases in rat spinal cord. PGFS I exists in neuronal somata and dendrites in the gray substance, and PGFS II exists in ependymal cells and tanycytes surrounding the central canal. Both enzymes are also present in endothelial cells of blood vessels in the white and gray substances of the spinal cord. In this study, we found that FP localizes in neuronal somata and dendrites but not in ependymal cells, tanycytes, or endothelial cells. Immunohistochemical analysis of serial sections showed the colocalization of FP and PGFS I. FP immunoreactivity was intense in spinal laminae I and II of the dorsal horn, a connection site of pain transmission, and was similar to that of PGFS I in neuronal elements. These findings suggest that prostaglandin F(2alpha) synthesized in the neuronal somata and dendrites exert an autocrine action there.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunocytochemical localization of prostaglandin F synthase II in the rat spinal cord.Brain Res. 2003 Apr 18;969(1-2):27-35. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)04244-0. Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12676361
-
Co-localization of prostaglandin F synthase, cyclooxygenase-1 and prostaglandin F receptor in mouse Leydig cells.Histochem Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;128(4):317-22. doi: 10.1007/s00418-007-0316-4. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Histochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17674023
-
Immunocytochemical localization of lung-type prostaglandin F synthase in the rat spinal cord.Brain Res. 2000 Sep 22;877(2):391-5. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02709-8. Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 10986358
-
Coupling between cyclooxygenases and prostaglandin F(2alpha) synthase. Detection of an inducible, glutathione-activated, membrane-bound prostaglandin F(2alpha)-synthetic activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Jul 21;1633(2):96-105. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(03)00092-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12880869
-
Prostaglandins and cyclooxygenases [correction of cycloxygenases] in the spinal cord.Prog Neurobiol. 2001 Jul;64(4):327-63. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(00)00063-0. Prog Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11275357 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin FP receptor antagonists: discovery, pharmacological characterization and therapeutic utility.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;176(8):1059-1078. doi: 10.1111/bph.14335. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29679483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The enzymology of the human prostanoid pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jun;47(6):4569-4586. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05526-z. Epub 2020 May 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32430846 Review.
-
Neuroaxonal and cellular damage/protection by prostanoid receptor ligands, fatty acid derivatives and associated enzyme inhibitors.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jan;18(1):5-17. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.343887. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 35799502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minami T., Uda R., Horiguchi S., Ito S., Hyodo M., Hayaishi O. 1992. Allodynia evoked by intrathecal administration of prostaglandin F2α to conscious mice. Pain. 50: 223–229. - PubMed
-
- Kimura H., Okamoto K., Sakai Y. 1985. Modulatory effects of prostaglandin D2, E2 and F2α on the postsynaptic actions of inhibitory and excitatory amino acids in cerebellar Purkinje cell dendrites in vitro. Brain Res. 330: 235–244. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K., Iguchi Y., Iguchi S., Arai Y., Hayaishi O., Roberts L. J., 2nd 1986. Stereospecific conversion of prostaglandin D2 to (5Z,13E)-(15S)-9 alpha-11 beta,15-trihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid (9α,11β-prostaglandin F2) and of prostaglandin H2 to prostaglandin F2α by bovine lung prostaglandin F synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83: 1583–1587. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suzuki T., Fujii Y., Miyano M., Chen L. Y., Takahashi T., Watanabe K. 1999. cDNA cloning, expression, and mutagenesis study of liver-type prostaglandin F synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 241–248. - PubMed
-
- Moriuchi H., Koda N., Okuda-Ashitaka E., Daiyasu H., Ogasawara K., Toh H., Ito S., Woodward D. F., Watanabe K. 2007. Molecular characterization of a novel type of prostamide/prostaglandin F synthase, belonging to the thioredoxin-like superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 283: 792–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

