Decapping is preceded by 3' uridylation in a novel pathway of bulk mRNA turnover
- PMID: 19430462
- PMCID: PMC2875167
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1601
Decapping is preceded by 3' uridylation in a novel pathway of bulk mRNA turnover
Abstract
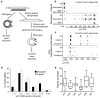
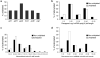
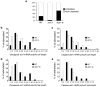
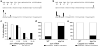
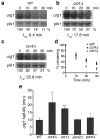
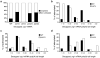
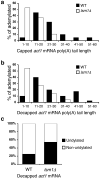
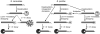
Both end structures of eukaryotic mRNAs, namely the 5' cap and 3' poly(A) tail, are necessary for transcript stability, and loss of either is sufficient to stimulate decay. mRNA turnover is classically thought to be initiated by deadenylation, as has been particularly well described in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Here we describe two additional, parallel decay pathways in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. First, in fission yeast mRNA decapping is frequently independent of deadenylation. Second, Cid1-dependent uridylation of polyadenylated mRNAs, such as act1, hcn1 and urg1, seems to stimulate decapping as part of a novel mRNA turnover pathway. Accordingly, urg1 mRNA is stabilized in cid1Delta cells. Uridylation and deadenylation act redundantly to stimulate decapping, and our data suggest that uridylation-dependent decapping is mediated by the Lsm1-7 complex. As human cells contain Cid1 orthologs, uridylation may form the basis of a widespread, conserved mechanism of mRNA decay.
Figures
Similar articles
-
3' Uridylation and the regulation of RNA function in the cytoplasm.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1150-3. doi: 10.1042/BST0381150. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20659020 Review.
-
Uridylation regulates mRNA decay directionality in fission yeast.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):8359. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50824-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39333464 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in translation initiation factors lead to increased rates of deadenylation and decapping of mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Aug;19(8):5247-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5247. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10409716 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast EDC1 mRNA undergoes deadenylation-independent decapping stimulated by Not2p, Not4p, and Not5p.EMBO J. 2005 Mar 9;24(5):1033-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600560. Epub 2005 Feb 10. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15706350 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and control of mRNA decapping in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:571-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.571. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10966469 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and mechanism of CutA, RNA nucleotidyl transferase with an unusual preference for cytosine.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 18;48(16):9387-9405. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa647. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32785623 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis Triggers Specific, Rapid, and Global mRNA Decay with 3' Uridylated Intermediates Degraded by DIS3L2.Cell Rep. 2015 May 19;11(7):1079-89. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.026. Epub 2015 May 7. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 25959823 Free PMC article.
-
Lsm proteins and Hfq: Life at the 3' end.RNA Biol. 2013 Apr;10(4):592-601. doi: 10.4161/rna.23695. Epub 2013 Feb 7. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23392247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coding regions affect mRNA stability in human cells.RNA. 2019 Dec;25(12):1751-1764. doi: 10.1261/rna.073239.119. Epub 2019 Sep 16. RNA. 2019. PMID: 31527111 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of molecular machines involved in deadenylation-dependent 5'-3' mRNA degradation.Front Genet. 2023 Oct 9;14:1233842. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1233842. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37876592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Decker CJ, Parker R. A turnover pathway for both stable and unstable mRNAs in yeast: evidence for a requirement for deadenylation. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1632–43. - PubMed
-
- Muhlrad D, Decker CJ, Parker R. Deadenylation of the unstable mRNA encoded by the yeast MFA2 gene leads to decapping followed by 5′-->3′ digestion of the transcript. Genes Dev. 1994;8:855–66. - PubMed
-
- Shyu AB, Belasco JG, Greenberg ME. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991;5:221–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

