Structure-activity relationship of cyanine tau aggregation inhibitors
- PMID: 19432420
- PMCID: PMC2745078
- DOI: 10.1021/jm900116d
Structure-activity relationship of cyanine tau aggregation inhibitors
Abstract
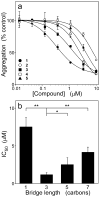
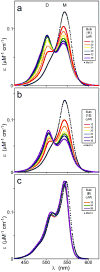
A structure-activity relationship for symmetrical cyanine inhibitors of human tau aggregation was elaborated using a filter trap assay. Antagonist activity depended on cyanine heterocycle, polymethine bridge length, and the nature of meso- and N-substituents. One potent member of the series, 3,3'-diethyl-9-methylthiacarbocyanine iodide (compound 11), retained submicromolar potency and had calculated physical properties consistent with blood-brain barrier and cell membrane penetration. Exposure of organotypic slices prepared from JNPL3 transgenic mice (which express human tau harboring the aggregation prone P301L tauopathy mutation) to compound 11 for one week revealed a biphasic dose response relationship. Low nanomolar concentrations decreased insoluble tau aggregates to half those observed in slices treated with vehicle alone. In contrast, high concentrations (> or =300 nM) augmented tau aggregation and produced abnormalities in tissue tubulin levels. These data suggest that certain symmetrical carbocyanine dyes can modulate tau aggregation in the slice biological model at concentrations well below those associated with toxicity.
Figures






References
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Buee L, Bussiere T, Buee-Scherrer V, Delacourte A, Hof PR. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000;33:95–130. - PubMed
-
- Congdon EE, Duff KE. Is tau aggregation toxic or protective? J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;14:453–457. - PubMed
-
- Kuret J. Detection and Reduction of Neurofibrillary Lesions. In: Smith HJ, Sewell RDE, Simons C, editors. Protein Folding Diseases: Enzyme Inhibitors and Other Agents as Prospective Therapies. Vol. 5. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Books; Boca Raton, FL: 2007. pp. 287–324.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

