Targeting a unique EGFR epitope with monoclonal antibody 806 activates NF-kappaB and initiates tumour vascular normalization
- PMID: 19432811
- PMCID: PMC4516546
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00783.x
Targeting a unique EGFR epitope with monoclonal antibody 806 activates NF-kappaB and initiates tumour vascular normalization
Abstract
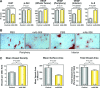
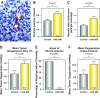
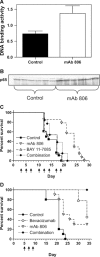
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is often pathogenetically overexpressed or mutated in epithelial malignancies and glioma, have been modestly successful, with some approved for human use. MAb 806 was raised against de2-7EGFR (or EGFRvIII), a constitutively active mutation expressed in gliomas, but also recognizes a subset (<10%) of wild-type (wt) EGFR when it is activated by autocrine loop, overexpression or mutation. It does not bind inactive EGFR in normal tissues like liver. Glioma xenografts expressing the de2-7EGFR treated with mAb 806 show reduced receptor autophosphorylation, increased p27(KIP1) and reduced cell proliferation. Xenografts expressing the wtEGFR activated by overexpression or autocrine ligand are also inhibited by mAb 806, but the mechanism of inhibition has been difficult to elucidate, especially because mAb 806 does not prevent wtEGFR phosphorylation or downstream signalling in vitro. Thus, we examined the effects of mAb 806 on A431 xenograft angiogenesis. MAb 806 increases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and interleukin-8 production by activating NF-kappaB and normalizes tumour vasculature. Pharmacological inhibition of NF-kappaB completely abrogated mAb 806 activity, demonstrating that NF-kappaB activation is necessary for its anti-tumour function in xenografts. Given the increase in VEGF, we combined mAb 806 with bevacizumab in vivo, resulting in additive activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NF-κB, interleukin-8 pathway.Oncogene. 2012 Sep 6;31(36):4054-66. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.563. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22139077 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the epitope for the epidermal growth factor receptor-specific monoclonal antibody 806 reveals that it preferentially recognizes an untethered form of the receptor.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 16;279(29):30375-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401218200. Epub 2004 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15075331
-
Novel monoclonal antibody specific for the de2-7 epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that also recognizes the EGFR expressed in cells containing amplification of the EGFR gene.Int J Cancer. 2002 Mar 20;98(3):398-408. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10189. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11920591
-
The epidermal growth factor receptor as a target for cancer therapy.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001 Mar;8(1):3-9. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0080003. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11350723 Review.
-
Monoclonal antibodies as effective therapeutic agents for solid tumors.Cancer Sci. 2004 Aug;95(8):621-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb03319.x. Cancer Sci. 2004. PMID: 15298722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Jun;15(2):420-34. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23575987 Review.
-
Targeting EGFR for treatment of glioblastoma: molecular basis to overcome resistance.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012 Mar;12(3):197-209. doi: 10.2174/156800912799277557. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22268382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal antibodies: versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 May;10(5):317-27. doi: 10.1038/nri2744. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20414205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine/Threonine Kinase MLK4 Determines Mesenchymal Identity in Glioma Stem Cells in an NF-κB-dependent Manner.Cancer Cell. 2016 Feb 8;29(2):201-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.01.005. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 26859459 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Receptors on Cancer Cells with Protein Toxins.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 17;10(9):1331. doi: 10.3390/biom10091331. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32957689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Libermann TA, Nusbaum HR, Razon N, et al. Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature. 1985;313:144–7. - PubMed
-
- Frederick L, Wang XY, Eley G, et al. Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1383–7. - PubMed
-
- Pedersen MW, Meltorn M, Damstrup L, et al. The type III epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Biological significance and potential target for anti-cancer therapy. Ann Oncol. 2001;12:745–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

