DR5-mediated DISC controls caspase-8 cleavage and initiation of apoptosis in human glioblastomas
- PMID: 19432816
- PMCID: PMC2891654
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00777.x
DR5-mediated DISC controls caspase-8 cleavage and initiation of apoptosis in human glioblastomas
Abstract
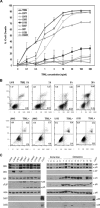
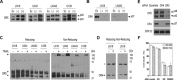
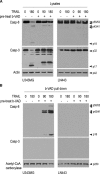
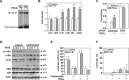
To explore the molecular mechanisms by which glioblastomas are resistant to tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), we examined TRAIL signalling pathways in the tumours. TRAIL has four membrane-anchored receptors, death receptor 4/5 (DR4/5) and decoy receptor 1/2 (DcR1/2). Of these receptors, only DR5 was expressed consistently in glioblastoma cell lines and tumour tissues, ruling out the role of DcR1/2 in TRAIL resistance. Upon TRAIL binding, DR5 was homotrimerized and recruited Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and caspase-8 for the assembly of death-inducing signalling complex (DISC) in the lipid rafts of the plasma membrane. In the DISC, caspase-8 was cleaved and initiated apoptosis by cleaving downstream caspases in TRAIL-sensitive glioblastoma cells. In TRAIL-resistant cells, however, DR5-mediated DISC was modified by receptor-interacting protein (RIP), cellular FADD-like interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) and phosphoprotein enriched in diabetes or in astrocyte-15 (PED/PEA-15). This DISC modification occurred in the non-raft fractions of the plasma membrane and resulted in the inhibition of caspase-8 cleavage and activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Treatment of resistant cells with parthenolide, an inhibitor of inhibitor of kappaB (I-kappaB), eliminated TRAIL-induced NF-kappaB activity but not TRAIL resistance. In contrast, however, targeting of RIP, c-FLIP or PED/PEA-15 with small interfering RNA (siRNA) led to the redistribution of the DISC from non-rafts to lipid rafts and eliminated the inhibition of caspase-8 cleavage and thereby TRAIL resistance. Taken together, this study indicates that the DISC modification by RIP, c-FLIP and PED/PEA-15 is the most upstream event in TRAIL resistance in glioblastomas.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipid rafts and nonrafts mediate tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand induced apoptotic and nonapoptotic signals in non small cell lung carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2007 Jul 15;67(14):6946-55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3896. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17638906
-
Human astrocytes are resistant to Fas ligand and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 22;26(12):3299-308. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5572-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16554480 Free PMC article.
-
Induction and intracellular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) mediated apotosis in human malignant glioma cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Feb 1;61(3):1162-70. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11221847
-
Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2005 Mar;12(3):228-37. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700792. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15550937 Review.
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
Cited by
-
A20 ubiquitin ligase-mediated polyubiquitination of RIP1 inhibits caspase-8 cleavage and TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma.Cancer Discov. 2012 Feb;2(2):140-55. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0172. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22585859 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming TRAIL Resistance for Glioblastoma Treatment.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 14;11(4):572. doi: 10.3390/biom11040572. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33919846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 induces cancer cell senescence.Cancer Res. 2011 Jan 15;71(2):506-15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1977. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21084274 Free PMC article.
-
PIM kinases mediate resistance of glioblastoma cells to TRAIL by a p62/SQSTM1-dependent mechanism.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 18;10(2):51. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1293-3. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30718520 Free PMC article.
-
K-Ras mutation-mediated IGF-1-induced feedback ERK activation contributes to the rapalog resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas.Cancer Lett. 2012 Sep 1;322(1):58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.02.005. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Cancer Lett. 2012. PMID: 22342683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96. - PubMed
-
- Lefranc F, Facchini V, Kiss R. Proautophagic drugs: a novel means to combat apoptosis-resistant cancers, with a special emphasis on glioblastomas. Oncologist. 2007;12:1395–403. - PubMed
-
- Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, et al. Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1624–36. - PubMed
-
- Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R. Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2411–22. - PubMed
-
- Hao C, Beguinot F, Condorelli G, et al. Induction and intracellular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) mediated apotosis in human malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1162–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

