Temporal and contextual orchestration of cardiac fate by WNT-BMP synergy and threshold
- PMID: 19432819
- PMCID: PMC3823001
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00774.x
Temporal and contextual orchestration of cardiac fate by WNT-BMP synergy and threshold
Abstract
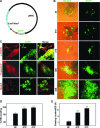
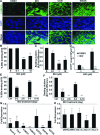
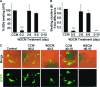
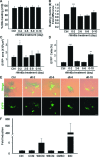
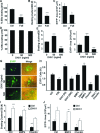
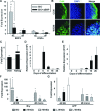
Cardiomyogenic development proceeds with a cascade of intricate signalling events that operate in a temporo-spatial fashion to specify cardiac cell fate during early embryogenesis. In fact, conflicting reports exist regarding the role of Wnt/β-catenin signalling during cardiomyogenesis. Here, we describe a dose-dependent and temporal effect of Wnt/β-catenin signalling on in vitro cardiomyogenesis using embryonic stem cells (ESCs) as a model system. We could demonstrate that canonical Wnt activation during early stage of differentiation either through ligand or by GSK3β inhibition helped in maintaining Oct4 and Nanog expressions, and in parallel, it promoted mesoderm and endoderm inductions. In contrast, it led to attenuation in cardiomyogenesis that was reversed by moderate concentration of DKK1, but not soluble Fz8. However, higher DKK1 could also block cardiomyogenesis, suggesting thereby governance of a particular signalling threshold underlying this developmental event. Interestingly, Wnt signalling activation at early stage modulated BMP4 expression in a stage-specific manner. Wnt activation, synchronized with BMP4 and brachyury up-regulation at early stage, correlated well with mesoderm induction. Conversely, Wnt activation led to BMP4 and Wnt5a down-regulation at late stage culminating in cardiomyogenic attenuation. Our findings suggested the existence of precise regulatory machinery with context-dependent role of Wnt for fine tuning mesoderm induction and its derivatives, through establishment of Wnt gradient during ESCs' differentiation. Moreover, contrary to mere activation/inhibition, a specific threshold of Wnt and BMP and their synergy seemed necessary for providing the guiding cues in orchestrating mesoderm induction and subsequent cardiomyogenesis.
© 2009 The Authors Journal compilation © 2010 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endogenous Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for cardiac differentiation in human embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 15;5(6):e11134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011134. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20559569 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of Tcf3 and Tcf1 control Wnt stimulation of embryonic stem cell self-renewal.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Jun 19;13(7):762-70. doi: 10.1038/ncb2283. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21685894 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal modulation of β-catenin signaling by multicellular aggregation kinetics impacts embryonic stem cell cardiomyogenesis.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Oct 1;22(19):2665-77. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0007. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23767804 Free PMC article.
-
Maintaining embryonic stem cell pluripotency with Wnt signaling.Development. 2011 Oct;138(20):4341-50. doi: 10.1242/dev.066209. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Development. 2011. PMID: 21903672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesodermal fate decisions of a stem cell: the Wnt switch.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Sep;65(17):2658-74. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8042-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18528633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclosporin A induces cardiac differentiation but inhibits hemato-endothelial differentiation of P19 cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 28;10(1):e0117410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117410. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25629977 Free PMC article.
-
Deleterious Rare Mutations of GLI1 Dysregulate Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Human Congenital Heart Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 4;9:798033. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.798033. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35445092 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Epitranscriptomic Signatures in Cell Fate Determination and Development.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019 Aug;15(4):474-496. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-09894-3. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019. PMID: 31123982 Review.
-
Elucidating the Anti-Tumorigenic Efficacy of Oltipraz, a Dithiolethione, in Glioblastoma.Cells. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):3057. doi: 10.3390/cells11193057. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231019 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Stem Cells as Therapeutics for Severe Mental Disorders and Cognitive Impairments.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 30;11:80. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00080. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32425815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schultheiss TM, Burch JB, Lassar AB. A role for bone morphogenetic proteins in the induction of cardiac myogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997;11:451–62. - PubMed
-
- Barro M, Gao M, Lough J. Requirement for BMP and FGF signaling during cardiogenic induction in non-precardiac mesoderm is specific, transient, and cooperative. Dev Dyn. 2000;218:383–93. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Katsev S, Cai C, Evans S. BMP signaling is required for heart formation in vertebrates. Dev Biol. 2000;224:226–37. - PubMed
-
- Choi M, Stottmann RW, Yang YP, et al. The bone morphogenetic protein antagonist noggin regulates mammalian cardiac morphogenesis. Circ Res. 2007;100:220–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

