Radiosensitizing effects of gefitinib at different administration times in vitro
- PMID: 19432883
- PMCID: PMC11159024
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01190.x
Radiosensitizing effects of gefitinib at different administration times in vitro
Abstract
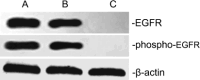
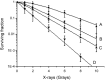
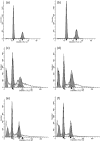
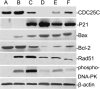
The optimal administration time for applying epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors combined with radiotherapy has been unclear. We investigated the efficacy of combining gefitinib with radiation in different treatment schedules. We demonstrated that gefitinib was administered to A549 lung cancer cells in three ways (administration before irradiation, administration upon irradiation, administration after irradiation) to establish the radiosensitizing effect. Cell-survival rates were evaluated by colony-forming assays. Cell apoptosis and cell-cycle distribution were investigated using flow cytometry; meanwhile, the expression of P21, Cdc25c, Bcl-2, Bax, Rad51 and phosphorylated DNA-PKcs (phospho-DNA-PK) after 6 Gy irradiation and/or gefitinib were determined by Western blot analysis. The sensitizer enhancement ratios of the gefitinib administration before irradiation, administration upon irradiation, and administration after irradiation groups were 2.23, 1.51 and 1.30, respectively. A higher apoptosis rate and G(2)/M phase arrest were observed in cells at 48 h after exposure to 6 Gy irradiation when gefitinib was administrated before irradiation. Increased cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest were further supported by the expression changes of Bcl-2, Bax, P21, Cdc25c, Rad51 and phospho-DNA-PK at the same time. The best radiosensitizing effect was obtained when gefitinib was delivered before irradiation. Apoptosis might be an important way of cell killing and G(2)/M phase arrest might be an important mechanism of apoptosis. The expression proportion changes of P21/Cdc25c proteins may play an important role in G(2)/M cell cycle arrest. Moreover, the pro-apoptotic/antiapoptotic and DNA repair factors may be important modulators taking part in the molecular events of the radiosensitizing effect of gefitinib combined with irradiation.
Figures
References
-
- Masui H, Kawamoto T, Sato JD et al . Growth inhibition of human tumor cells in athymic mice by anti‐epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res 1984; 44: 1002–7. - PubMed
-
- Yaish P, Gazit A, Gilon C et al . Blocking of EGF‐dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science 1988; 242: 933–5. - PubMed
-
- Gschwind A, Fischer OM, Ullrich A. The discovery of receptor tyrosine kinases: targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 361–70. - PubMed
-
- Jose B. Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway inhibitors. Update on Cancer Therapeut 2006; 1: 299–310.
-
- Fortunato C, Giampaolo T. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1160–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

