Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor stimulation enhances the multifunctionality of adoptively transferred tumor antigen-specific CD8+ T cells with tumor regression
- PMID: 19432889
- PMCID: PMC11158648
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01179.x
Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor stimulation enhances the multifunctionality of adoptively transferred tumor antigen-specific CD8+ T cells with tumor regression
Abstract
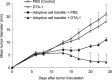
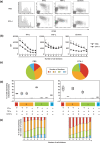
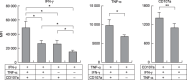
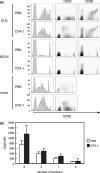
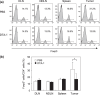
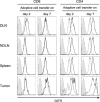
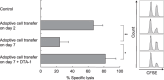
We have reported for the first time the significance of effector T-cell multifunctionality in antitumor immunity, suggesting that the appearance of multifunctional/polyfunctional tumor-specific CD8(+) T cells in vivo is a critical determinant of the success of antitumor immunotherapy, and a strategy to induce multifunctionality in effector cells is required for the successful immunotherapy of hosts with progressing tumor. Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (GITR) stimulation has been shown to enhance antitumor immune response. However, its functional impact on adoptively transferred T cells remains unclear. Here, we analyzed the impact of GITR stimulation in vivo on the functional profiles of adoptively transferred CD8(+) T cells specific for murine fibrosarcoma CMS5. GITR stimulation was found to enhance multifunctionality (interferon (IFN)-gamma and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production and CD107a mobilization as a degranulation marker) in transferred cells at the single-cell level. These cells exhibited upregulated expression of CD25 in draining lymph nodes and increased infiltration in tumor. Mice that received T-cell therapy with GITR stimulation showed reduced Foxp3(+)CD4(+) T cells among tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and increased in vivo cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) activity even with progressing tumor, resulting in enhanced tumor regression. These data strengthen the idea that effector T-cell multifunctionality is a sensitive immune correlate for successful immunotherapy against malignancy and provide an immunological rationale for effective T-cell therapy combined with GITR stimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor progression inhibits the induction of multifunctionality in adoptively transferred tumor-specific CD8+ T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Jan;39(1):241-53. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838824. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19089817
-
Pivotal roles of CD4+ effector T cells in mediating agonistic anti-GITR mAb-induced-immune activation and tumor immunity in CT26 tumors.J Immunol. 2007 Dec 1;179(11):7365-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.11.7365. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18025180
-
Agonist anti-GITR monoclonal antibody induces melanoma tumor immunity in mice by altering regulatory T cell stability and intra-tumor accumulation.PLoS One. 2010 May 3;5(5):e10436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010436. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20454651 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of CTLA-4 and GITR for cancer immunotherapy.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;344:211-44. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_49. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20563707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related (GITR) protein and its ligand in antitumor immunity: functional role and therapeutic modulation.Clin Dev Immunol. 2010;2010:239083. doi: 10.1155/2010/239083. Epub 2010 Sep 26. Clin Dev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20936139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting tumor-necrosis factor receptor pathways for tumor immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2014 Apr 15;2:7. doi: 10.1186/2051-1426-2-7. eCollection 2014. J Immunother Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24855562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving Adoptive T Cell Therapy: The Particular Role of T Cell Costimulation, Cytokines, and Post-Transfer Vaccination.Front Immunol. 2016 Sep 6;7:345. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00345. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27656185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy targeting a MAGE A4 peptide and HLA-A*02:01 complex for unresectable advanced or recurrent solid cancer: protocol for a multi-institutional phase 1 clinical trial.BMJ Open. 2022 Nov 14;12(11):e065109. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065109. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36375974 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering bionic T cells: signal 1, signal 2, signal 3, reprogramming and the removal of inhibitory mechanisms.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Jun;17(6):576-586. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0464-1. Epub 2020 May 20. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32433539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4+ T cells support polyfunctionality of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells with memory potential in immunological control of tumor.Cancer Sci. 2020 Jun;111(6):1958-1968. doi: 10.1111/cas.14420. Epub 2020 May 12. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32304127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darrah PA, Patel DT, De Luca PM et al . Multifunctional TH1 cells define a correlate of vaccine‐mediated protection against Leishmania major . Nat Med 2007; 13: 843–50. - PubMed
-
- De Rosa SC, Lu FX, Yu J et al . Vaccination in humans generates broad T cell cytokine responses. J Immunol 2004; 173: 5372–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

