Global DNA hypomethylation suppresses squamous carcinogenesis in the tongue and esophagus
- PMID: 19432896
- PMCID: PMC11158800
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01171.x
Global DNA hypomethylation suppresses squamous carcinogenesis in the tongue and esophagus
Abstract
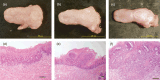
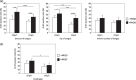
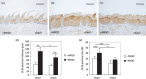
Genome-wide DNA hypomethylation and concomitant site-specific gene hypermethylation are among the most common molecular alterations in human neoplasia. Previous studies revealed that genetic reduction of the DNA methylation level results in opposing effects on tumor development, depending on the tumor cell type and on the different stages of the tumorigenesis. For instance, reduced levels of DNA methylation in mice strongly inhibited tumor development of the intestine, whereas they induced thymic lymphomas and liver tumors. In the present study, using DNA methyltrasferase 1 (Dnmt1) hypomorphic alleles to reduce genomic methylation, we examined the effects of DNA hypomethylation on a murine squamous carcinogenesis in the tongue and esophagus induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Genetic reduction of DNA methylation level led to the suppression of tumor formation in both tongue and esophagus. Histological analyses revealed that DNA hypomethylation preferentially inhibited the development of squamous cell carcinomas. The results suggest that genomic hypomethylation inhibits squamous carcinogenesis in the tongue and esophagus, and that pharmacological modification of epigenetic status might be useful for the prevention and treatment of cancers in the upper digestive tract.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral cavity and esophageal carcinogenesis modeled in carcinogen-treated mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jan 1;10(1 Pt 1):301-13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-0999-3. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 14734483
-
Black raspberries demethylate Sfrp4, a WNT pathway antagonist, in rat esophageal squamous cell papilloma.Mol Carcinog. 2016 Nov;55(11):1867-1875. doi: 10.1002/mc.22435. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Mol Carcinog. 2016. PMID: 27696538
-
High frequency methylation of p16INK4A gene during 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced rat tongue carcinogenesis.Oncol Rep. 2004 Jul;12(1):101-6. Oncol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15201967
-
Host genes controlling the susceptibility and resistance to squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in a rat model.Pathol Int. 2000 May;50(5):353-62. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2000.01058.x. Pathol Int. 2000. PMID: 10849324 Review.
-
Review of the alterations in DNA methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Surg Today. 2013 Dec;43(12):1355-64. doi: 10.1007/s00595-012-0451-y. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Surg Today. 2013. PMID: 23291904 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers of head and neck cancer, tools or a gordian knot?Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):10340-57. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophageal Cancer: Insights From Mouse Models.Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2015 Aug 16;8(Suppl 1):37-46. doi: 10.4137/CGM.S21218. eCollection 2015. Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2015. PMID: 26380556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing DNA methyltransferase 1 leads to the activation of the esophageal suppressor gene p16 in vitro and in vivo.Oncol Lett. 2017 Sep;14(3):3077-3081. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6535. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28927055 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation in peripheral blood: a potential biomarker for cancer molecular epidemiology.J Epidemiol. 2012;22(5):384-94. doi: 10.2188/jea.je20120003. Epub 2012 Aug 4. J Epidemiol. 2012. PMID: 22863985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell technology for dissecting the cancer epigenome.Cancer Sci. 2015 Oct;106(10):1251-6. doi: 10.1111/cas.12758. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26224327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 415–28. - PubMed
-
- Chen RZ, Pettersson U, Beard C, Jackson‐Grusby L, Jaenisch R. DNA hypomethylation leads to elevated mutation rates. Nature 1998; 395: 89–93. - PubMed
-
- Laird PW, Jackson‐Grusby L, Fazeli A et al . Suppression of intestinal neoplasia by DNA hypomethylation. Cell 1995; 81: 197–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

