Nucleic acid distribution pattern as a possible biomarker for metabolic activities of neoplastic cells: a digitally-aided fluorescence microscopy study on normal and neoplastic lymphocytes of acute and chronic canine lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 19432993
- PMCID: PMC2694150
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2867-9-13
Nucleic acid distribution pattern as a possible biomarker for metabolic activities of neoplastic cells: a digitally-aided fluorescence microscopy study on normal and neoplastic lymphocytes of acute and chronic canine lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
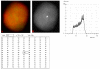
Background: Metabolic states of neoplastic cells are increasingly being relied upon for diagnostic and prognostic assessment of neoplastic conditions. The nucleic acid distribution pattern of cells in general, in terms of degree of condensation of the nuclear chromatin and overall spread of the nucleic acid within the nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments, can reflect the metabolic state of the cell. This simple but logical concept appears not be put into consideration to date as numerous attempts are being made towards formulating reliable biomarkers for rapid diagnosis, prognosis and subsequent therapeutic interventions for neoplastic conditions. We comparatively evaluated nucleic acid distribution patterns of normal lymphocytes and neoplastic cells of lymphocytic lineage, employing light and fluorescence microscopy procedures, as well as digital imaging analytical methods.
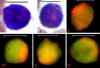
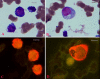
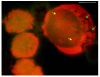
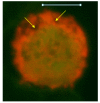
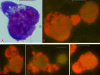
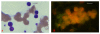
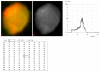
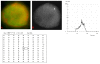
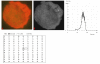
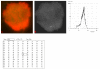
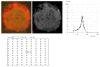
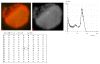
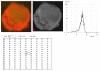
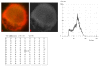
Results: The results demonstrate distinctiveness in the pattern of nucleic acid distribution for the normal lymphocytes and three lymphocytic neoplastic cell-types of canine lymphocytic leukemia that are categorized as small, intermediate and large neoplastic lymphocytes. Variably-shaped cytoplasmic processes laden with single-stranded nucleic acids (SSNA) were observed for the small and intermediate-sized neoplastic lymphocytes, compared with large neoplastic lymphocytes and the normal lymphocytes; the latter two categories of cells being virtually devoid of similar processes. Prominent cytoplasmic and nuclear clumps of SSNA, indicative of a higher rate of metabolic activity, were also observed within the neoplastic cells compared with fewer and narrower SSNA of the normal cells.
Conclusion: The comparative relative increases of SSNA in cytoplasmic processes and other cellular areas of small and intermediate-sized neoplastic lymphocytes is reflective of greater metabolic activity in neoplastic cells in general compared with their normal cellular counterparts.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nucleic acid distribution pattern in avian erythrocytes and mammalian lymphocytes: comparative studies by fluorescence microscopy and digital imaging analytical techniques.Res Vet Sci. 2008 Dec;85(3):418-32. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2008.03.004. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Res Vet Sci. 2008. PMID: 18448142
-
BIOLOGICAL STUDIES OF THE TUBERCLE BACILLUS : II. A NEW CONCEPTION OF THE PATHOLOGY OF EXPERIMENTAL AVIAN TUBERCULOSIS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE DISEASE PRODUCED BY DISSOCIATED VARIANTS.J Exp Med. 1933 Jan 31;57(2):239-64. doi: 10.1084/jem.57.2.239. J Exp Med. 1933. PMID: 19870129 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear morphologic and morphometric analyses of nodular poorly differentiated lymphocytic lymphoma: assessment of small cleaved nuclei.Hum Pathol. 1985 Dec;16(12):1187-99. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80030-7. Hum Pathol. 1985. PMID: 3905575
-
Release of viruses and viral DNA from nucleus to cytoplasm of HeLa cells at late stages of productive adenovirus infection as revealed by electron microscope in situ hybridization.Biol Cell. 1998 Jan;90(1):5-38. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(98)80230-x. Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9691424 Review.
-
Characteristics of heterogeneous nuclear RNA in normal small lymphocytes and in acute leukemia blast cells. An outline.Acta Haematol. 1975;54(4):234-41. doi: 10.1159/000208080. Acta Haematol. 1975. PMID: 811037 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

