IQGAPs in cancer: a family of scaffold proteins underlying tumorigenesis
- PMID: 19433088
- PMCID: PMC2743239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.05.007
IQGAPs in cancer: a family of scaffold proteins underlying tumorigenesis
Abstract
The IQGAP family comprises three proteins in humans. The best characterized is IQGAP1, which participates in protein-protein interactions and integrates diverse signaling pathways. IQGAP2 and IQGAP3 harbor all the domains identified in IQGAP1, but their biological roles are poorly defined. Proteins that bind IQGAP1 include Cdc42 and Rac1, E-cadherin, beta-catenin, calmodulin and components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, all of which are involved in cancer. Here, we summarize the biological functions of IQGAPs that may contribute to neoplasia. Additionally, we review published data which implicate IQGAPs in cancer and tumorigenesis. The cumulative evidence suggests IQGAP1 is an oncogene while IQGAP2 may be a tumor suppressor.
Figures
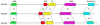
References
-
- Briggs MW, Sacks DB. IQGAP1 as signal integrator: Ca2+, calmodulin, Cdc42 and the cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett. 2003;542:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Weissbach L, Settleman J, Kalady MF, Snijders AJ, Murthy AE, Yan YX, Bernards A. Identification of a human RasGAP-related protein containing calmodulin-binding motifs. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20517–21. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, et al. IQGAP3, a novel effector of Rac1 and Cdc42, regulates neurite outgrowth. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:567–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

