Adherence to long-term surveillance mammography among women with ductal carcinoma in situ treated with breast-conserving surgery
- PMID: 19433691
- PMCID: PMC2716942
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.5876
Adherence to long-term surveillance mammography among women with ductal carcinoma in situ treated with breast-conserving surgery
Abstract
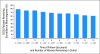
PURPOSE Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) is an effective treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) but women who undergo BCS remain at risk for recurrences. Whether mammographic surveillance after BCS occurs and by whom is not known. METHODS We reviewed medical records of women diagnosed with DCIS between 1990 and 2001 and treated with BCS. Using descriptive statistics, generalized estimating, and logistic regression modeling, we examined the rates and predictors of surveillance mammography over a 10-year period after BCS. Results The cohort included 3,037 women observed for a median of 4.8 years (range, 0.5 to 15.7). Of the 2,676 women observed for at least 1 year after BCS, most (79%) had at least one surveillance mammogram during the first year of follow-up; 69% in year 5 and 61% in year 10. Among those observed for 5 years, surveillance mammograms were more likely among women age 60 to 69 years (odds ratio [OR], 1.72; 95% CI, 1.26 to 2.34), users of menopausal hormone therapy at diagnosis (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.57) as well as those treated with adjuvant radiation (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.08 to 1.53) and adjuvant radiation with tamoxifen (OR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.13 to 2.30). Surveillance mammograms were less likely among obese women (OR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.56 to 0.86). The findings were similar among women observed for 10 years. Only 34% and 15% of women observed for 5 and 10 years, respectively, had a surveillance mammogram during each year of follow-up. CONCLUSION Surveillance mammography after BCS among insured women with DCIS often did not occur yearly and declined over time after treatment. Patients and providers must remain vigilant about surveillance after BCS.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society: Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2007-2008. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society Inc; http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/BCFF-Final.pdf.
-
- Burstein HJ, Polyak K, Wong JS, et al. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1430–1431. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Costantino J, Redmond C, et al. Lumpectomy compared with lumpectomy and radiation therapy for the treatment of intraductal breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1581–1586. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, et al. Tamoxifen in treatment of intraductal breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-24 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1999;353:1993–2000. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, et al. Lumpectomy and radiation therapy for the treatment of intraductal breast cancer: Findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-17. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:441–452. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical