Functional role of CD11c+ monocytes in atherogenesis associated with hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 19433759
- PMCID: PMC2716173
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.823740
Functional role of CD11c+ monocytes in atherogenesis associated with hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
Background: Monocyte activation and migration into the arterial wall are key events in atherogenesis associated with hypercholesterolemia. CD11c/CD18, a beta2 integrin expressed on human monocytes and a subset of mouse monocytes, has been shown to play a distinct role in human monocyte adhesion on endothelial cells, but the regulation of CD11c in hypercholesterolemia and its role in atherogenesis are unknown.
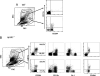
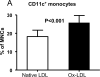
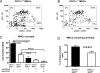
Methods and results: Mice genetically deficient in CD11c were generated and crossbred with apolipoprotein E (apoE)-/- mice to generate CD11c-/-/apoE-/- mice. Using flow cytometry, we examined CD11c on blood leukocytes in apoE-/- hypercholesterolemic mice and found that compared with wild-type and apoE-/- mice on a normal diet, apoE-/- mice on a Western high-fat diet had increased CD11c+ monocytes. Circulating CD11c+ monocytes from apoE-/- mice fed a high-fat diet exhibited cytoplasmic lipid vacuoles and expressed higher levels of CD11b and CD29. Deficiency of CD11c decreased firm arrest of mouse monocytes on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin in a shear flow assay, reduced monocyte/macrophage accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions, and decreased atherosclerosis development in apoE-/- mice on a high-fat diet.
Conclusions: CD11c, which increases on blood monocytes during hypercholesterolemia, plays an important role in monocyte recruitment and atherosclerosis development in an apoE-/- mouse model of hypercholesterolemia.
Figures











References
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:678–689. - PubMed
-
- Zhao L, Moos MP, Grabner R, Pedrono F, Fan J, Kaiser B, John N, Schmidt S, Spanbroek R, Lotzer K, Huang L, Cui J, Rader DJ, Evans JF, Habenicht AJ, Funk CD. The 5-lipoxygenase pathway promotes pathogenesis of hyperlipidemia-dependent aortic aneurysm. Nat Med. 2004;10:966–973. - PubMed
-
- Nageh MF, Sandberg ET, Marotti KR, Lin AH, Melchior EP, Bullard DC, Beaudet AL. Deficiency of inflammatory cell adhesion molecules protects against atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17:1517–1520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL098839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY007551/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY017120/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047294/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL042550/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL082689/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EY017120/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062243/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL62243-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL082689/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL086350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL42550/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 HL072754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

