RNAi screen for rapid therapeutic target identification in leukemia patients
- PMID: 19433805
- PMCID: PMC2680429
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903233106
RNAi screen for rapid therapeutic target identification in leukemia patients
Abstract
Targeted therapy has vastly improved outcomes in certain types of cancer. Extension of this paradigm across a broad spectrum of malignancies will require an efficient method to determine the molecular vulnerabilities of cancerous cells. Improvements in sequencing technology will soon enable high-throughput sequencing of entire genomes of cancer patients; however, determining the relevance of identified sequence variants will require complementary functional analyses. Here, we report an RNAi-assisted protein target identification (RAPID) technology that individually assesses targeting of each member of the tyrosine kinase gene family. We demonstrate that RAPID screening of primary leukemia cells from 30 patients identifies targets that are critical to survival of the malignant cells from 10 of these individuals. We identify known, activating mutations in JAK2 and K-RAS, as well as patient-specific sensitivity to down-regulation of FLT1, CSF1R, PDGFR, ROR1, EPHA4/5, JAK1/3, LMTK3, LYN, FYN, PTK2B, and N-RAS. We also describe a previously undescribed, somatic, activating mutation in the thrombopoietin receptor that is sensitive to down-stream pharmacologic inhibition. Hence, the RAPID technique can quickly identify molecular vulnerabilities in malignant cells. Combination of this technique with whole-genome sequencing will represent an ideal tool for oncogenic target identification such that specific therapies can be matched with individual patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare a conflict of interest (such as defined by PNAS policy). Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) and B.J.D. have a financial interest in MolecularMD. Technology used in this research has been licensed to MolecularMD. This potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by the OHSU Conflict of Interest in Research Committee and the Integrity Program Oversight Council.
Figures
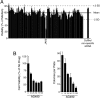
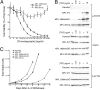


References
-
- Druker BJ, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Smith I, et al. 2-year follow-up of trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;369:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Krause DS, Van Etten RA. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:172–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

