Cycle-specific organocascade catalysis: application to olefin hydroamination, hydro-oxidation, and amino-oxidation, and to natural product synthesis
- PMID: 19434637
- PMCID: PMC3057093
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.200900220
Cycle-specific organocascade catalysis: application to olefin hydroamination, hydro-oxidation, and amino-oxidation, and to natural product synthesis
Abstract
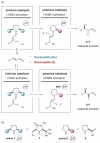
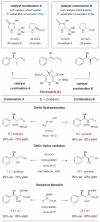
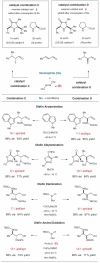
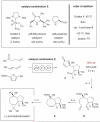
United in effort: The combined application of iminium (Im) and enamine (En) catalysts can effect a range of valuable asymmetric transformations including 1,2-hydroamination, -hydro-oxidation, and -amino-oxidation of olefins (see picture). An enantioselective organocascade catalysis was also applied in the synthesis of a complex natural product.
Figures
References
-
- Wender PA, Bi FC, Gamber GG, Gosselin F, Hubbard RD, Scanio MJC, Sun R, Williams TJ. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002;74:25–31.
- MacMillan DWC, Walji AM. Synlett. 2007:1477–1489.
-
-
“Organocascade catalysis” describes the merger of two discrete organocatalytic cycles, each of which is involved the generation of stereogenic centers. For a comprehensive description see reference [1b].
-
-
-
Organocascade catalysis: Huang Y, Walji AM, Larsen CH, MacMillan DWC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:15051–15053.. Several related manuscripts were submitted shortly after: Zhou J, List B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:15035–15037.; Marigo M, Schulte T, Fránzen J, Jørgensen KA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:15710–15711.
-
-
- Chi Y, Scroggins ST, Fréchet JMJ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:6322–6323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

