Cervical carotid and circle of willis arterial anatomy of macaque monkeys: a comparative anatomy study
- PMID: 19434671
- PMCID: PMC2743742
- DOI: 10.1002/ar.20891
Cervical carotid and circle of willis arterial anatomy of macaque monkeys: a comparative anatomy study
Abstract
Macaque monkeys are used in many research applications, including cerebrovascular investigations. However, detailed catalogs of the relevant vascular anatomy are scarce. We present our experience with macaque vessel patterns as determined by digital subtraction angiography of 34 different monkeys. We retrospectively analyzed digital subtraction angiograms obtained during experimental internal carotid artery (ICA) catheterization and subsequent injection of 1-methyl 4-phenyl 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Results were catalogued according to vascular distribution and variants observed. Macaque monkeys have a bovine aortic arch. The carotid vessels generally bifurcate, but are occasionally observed to divide into three vessels. The external carotid gives rise primarily to two trunks: an occipital branch and a common vessel that subsequently gives off the lingual, facial, and superior thyroid arteries. The internal maxillary artery may be present as a terminal branch of the external carotid or as a branch of the occipital artery. The ICA is similar in course to that of the human. The anterior circle of Willis was intact in all monkeys in our study. Its primary difference from that of the human is the union of the bilateral anterior cerebral arteries as a single (azygous) median vessel. Macaque cervical carotid and circle of Willis arterial anatomy differs from humans in a couple of specific patterns. Knowledge of these differences and similarities between human and macaque anatomy is important in developing endovascular macaque models of human diseases, such as ischemic stroke.
Figures



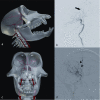
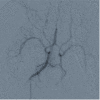
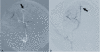


Comment in
-
Bovine aortic arch: in search of a more appropriate name.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009 Nov;292(11):1699. doi: 10.1002/ar.20947. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2009. PMID: 19718719 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beere PA, Glagov S, Zarins CK. Experimental atherosclerosis at the carotid bifurcation of the cynomolgus monkey. Localization, compensatory enlargement, and the sparing effect of lowered heart rate. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992;12:1245–53. - PubMed
-
- Brassel F, Dettmers C, Nierhaus A, Hartmann A, Solymosi L. An intravascular technique to occlude the middle cerebral artery in baboons. Neuroradiology. 1989;31:418–24. - PubMed
-
- Bremer AM, Watanabe O, Bourke RS. Artificial embolization of the middle cerebral artery in primates. Description of an experimental model with extracranial technique. Stroke. 1975;6:387–90. - PubMed
-
- Coceani F, Gloor P. The distribution of the internal carotid circulation in the brain of the macaque monkey (Macaca mulatta) J Comparative Neurol. 1966;128:419–429.
-
- Diener HC, Lees KR, Lyden P, Grotta J, Davalos A, Davis SM, Shuaib A, Ashwood T, Wasiewski W, Alderfer V, Hårdemark HG, Rodichok L, SAINT I and II Investigators NXY-059 for the treatment of acute stroke: pooled analysis of the SAINT I and II Trials. Stroke. 2008;39:1751–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

