Quality of life in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: baseline data from the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network
- PMID: 19434741
- PMCID: PMC2692572
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.22868
Quality of life in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: baseline data from the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network
Abstract
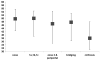
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease in the United States. The association between NAFLD and quality of life (QOL) remains unclear. These data are important to estimate the burden of illness in NAFLD. The aim was to report QOL scores of adults with NAFLD and examine the association between NAFLD severity and QOL. QOL data were collected from adults with NAFLD enrolled in the Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network using the Short Form 36 (SF-36) survey, and scores were compared with normative U.S. population scores. Liver biopsy histology was reviewed by a central pathology committee. A total of 713 subjects with NAFLD (male = 269, female = 444) were included. Mean age of subjects was 48.3 years; 61% had definite nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and 28% had bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis. Diabetes was present in 27% of subjects. Subjects with NAFLD had worse physical (mean, 45.2) and mental health scores (mean, 47.6) compared with the U.S. population with (mean, 50) and without (physical, 55.8; mental, 52.5) chronic illness. Subjects with NASH reported lower physical health compared with subjects with fatty liver disease without NASH (44.5 versus 47.1, P = 0.02). Subjects with cirrhosis had significantly (P < 0.001) poorer physical health scores (38.4) than subjects with no (47.6), mild (46.2), moderate (44.6), or bridging fibrosis (44.6). Cirrhosis was associated with poorer physical health after adjusting for potential confounders. Mental health scores did not differ between participants with and without NASH or by degree of fibrosis.
Conclusion: Adults with NAFLD have a significant decrement in QOL. Treatment of NAFLD should incorporate strategies to improve QOL, especially physical health.
Figures


References
-
- American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1702–1704. - PubMed
-
- Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM. The prevalence and etiology of elevated aminotransferase levels in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:960–967. - PubMed
-
- Kim WR, Brown RS, Jr, Terrault NA, El-Serag H. Burden of liver disease in the United States: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2002;36:227–242. - PubMed
-
- Ioannou GN, Boyko EJ, Lee SP. The prevalence and predictors of elevated serum aminotransferases activity in the United States in 1999–2002. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:76–82. - PubMed
-
- Bell BP, Manos MM, Zaman A, Terrault N, Thomas A, Navarro VJ, et al. The Epidemiology of Newly Diagnosed Chronic Liver Disease in Gastroenterology Practices in the United States: Results From Population-Based Surveillance. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:2727–2736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1RR02501401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK002957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR0241301/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000065/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000827/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
