A network-based integrative approach to prioritize reliable hits from multiple genome-wide RNAi screens in Drosophila
- PMID: 19435510
- PMCID: PMC2697172
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-220
A network-based integrative approach to prioritize reliable hits from multiple genome-wide RNAi screens in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: The recently developed RNA interference (RNAi) technology has created an unprecedented opportunity which allows the function of individual genes in whole organisms or cell lines to be interrogated at genome-wide scale. However, multiple issues, such as off-target effects or low efficacies in knocking down certain genes, have produced RNAi screening results that are often noisy and that potentially yield both high rates of false positives and false negatives. Therefore, integrating RNAi screening results with other information, such as protein-protein interaction (PPI), may help to address these issues.
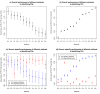
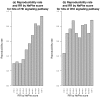
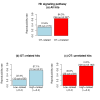
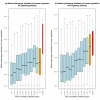
Results: By analyzing 24 genome-wide RNAi screens interrogating various biological processes in Drosophila, we found that RNAi positive hits were significantly more connected to each other when analyzed within a protein-protein interaction network, as opposed to random cases, for nearly all screens. Based on this finding, we developed a network-based approach to identify false positives (FPs) and false negatives (FNs) in these screening results. This approach relied on a scoring function, which we termed NePhe, to integrate information obtained from both PPI network and RNAi screening results. Using a novel rank-based test, we compared the performance of different NePhe scoring functions and found that diffusion kernel-based methods generally outperformed others, such as direct neighbor-based methods. Using two genome-wide RNAi screens as examples, we validated our approach extensively from multiple aspects. We prioritized hits in the original screens that were more likely to be reproduced by the validation screen and recovered potential FNs whose involvements in the biological process were suggested by previous knowledge and mutant phenotypes. Finally, we demonstrated that the NePhe scoring system helped to biologically interpret RNAi results at the module level.
Conclusion: By comprehensively analyzing multiple genome-wide RNAi screens, we conclude that network information can be effectively integrated with RNAi results to produce suggestive FPs and FNs, and to bring biological insight to the screening results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A protein network-guided screen for cell cycle regulators in Drosophila.BMC Syst Biol. 2011 May 6;5:65. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-65. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21548953 Free PMC article.
-
An effective method for controlling false discovery and false nondiscovery rates in genome-scale RNAi screens.J Biomol Screen. 2010 Oct;15(9):1116-22. doi: 10.1177/1087057110381783. Epub 2010 Sep 20. J Biomol Screen. 2010. PMID: 20855561
-
Drosophila genome-wide RNAi screens: are they delivering the promise?Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:141-8. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.027. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381290 Review.
-
The use of SSMD-based false discovery and false nondiscovery rates in genome-scale RNAi screens.J Biomol Screen. 2010 Oct;15(9):1123-31. doi: 10.1177/1087057110381919. Epub 2010 Sep 17. J Biomol Screen. 2010. PMID: 20852024
-
A Guide to Genome-Wide In Vivo RNAi Applications in Drosophila.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1478:117-143. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6371-3_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27730578 Review.
Cited by
-
The Drp1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fission Protein Interactome as an Emerging Core Player in Mitochondrial Dynamics and Cardiovascular Disease Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5785. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065785. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo RNAi-Based Screens: Studies in Model Organisms.Genes (Basel). 2013 Nov 25;4(4):646-65. doi: 10.3390/genes4040646. Genes (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24705267 Free PMC article.
-
FlyRNAi.org--the database of the Drosophila RNAi screening center: 2012 update.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D715-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr953. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22067456 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative approaches for predicting protein function and prioritizing genes for complex phenotypes using protein interaction networks.Brief Bioinform. 2014 Sep;15(5):685-98. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbt041. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Brief Bioinform. 2014. PMID: 23788799 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing molecular mechanisms by integrating high-dimensional functional screens with protein interaction data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Sep 4;10(9):e1003801. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003801. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25188415 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

