Failures to reconsolidate memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19435612
- PMCID: PMC2772829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2009.05.001
Failures to reconsolidate memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
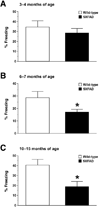
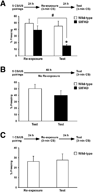
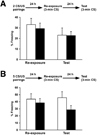
Previous studies have demonstrated that the formation of spatial, contextual and trace conditioning memories are impaired in animal models of Alzheimer's disease (AD), consistent with the observations that the first sign of cognitive decline in AD includes difficulties in the acquisition of new information or memory formation. Evidence is accumulating that memory retrieval is a dynamic process in which stored information becomes labile again and needs to be restabilized. However, it is poorly understood how this process referred to as memory reconsolidation is affected in animal models of AD. The present study was designed to use contextual fear conditioning to compare the changes in memory formation and subsequent reconsolidation processes in transgenic mice that overexpress human APP and PS1 harboring five familial AD mutations (5XFAD model). The results clearly demonstrate that cognitive dysfunction starts to occur primarily as reduced levels of contextual learning or memory formation in 5XFAD mice, but it is exacerbated by additional retrieval-dependent retrograde amnesia due to deficient reconsolidation as disease further develops.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic reductions of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and amyloid-beta ameliorate impairment of conditioned taste aversion memory in 5XFAD Alzheimer's disease model mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Jan;31(1):110-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.07031.x. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20092558 Free PMC article.
-
Impairments in remote memory stabilization precede hippocampal synaptic and cognitive failures in 5XFAD Alzheimer mouse model.Neurobiol Dis. 2009 Feb;33(2):229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.10.006. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2009. PMID: 19026746 Free PMC article.
-
Intraneuronal beta-amyloid accumulation in the amygdala enhances fear and anxiety in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar 15;67(6):513-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.06.015. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 19664757
-
Partial reduction of BACE1 improves synaptic plasticity, recent and remote memories in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice.J Neurochem. 2010 Apr;113(1):248-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06608.x. Epub 2010 Jan 20. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20089133 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of accelerated senescence on learning and memory, locomotion and anxiety-like behavior in APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Dec 15;335(1-2):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.09.018. Epub 2013 Sep 21. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24095271
Cited by
-
Dietary Wheat Amylase Trypsin Inhibitors Impact Alzheimer's Disease Pathology in 5xFAD Model Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6288. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176288. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878020 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated long-term forgetting: A sensitive paradigm for detecting subtle cognitive impairment and evaluating BACE1 inhibitor efficacy in preclinical Alzheimer's disease.Front Dement. 2023 Apr 18;2:1161875. doi: 10.3389/frdem.2023.1161875. eCollection 2023. Front Dement. 2023. PMID: 39081986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospho-eIF2α level is important for determining abilities of BACE1 reduction to rescue cholinergic neurodegeneration and memory defects in 5XFAD mice.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 23;5(9):e12974. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012974. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20886088 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic degeneration as revealed by PSD-95 reduction occurs after advanced Aβ and tau pathology in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2011 Sep;122(3):285-92. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0843-x. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Acta Neuropathol. 2011. PMID: 21630115 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cell transplantation improves spatial learning and memory via neuronal regeneration in amyloid-β precursor protein/presenilin 1/tau triple transgenic mice.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2014 Mar;29(2):142-9. doi: 10.1177/1533317513506776. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2014. PMID: 24265106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberini CM. Mechanisms of memory stabilization: are consolidation and reconsolidation similar or distinct processes? Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:51–56. - PubMed
-
- Ashe KH. Learning and memory in transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer's disease. Learn Mem. 2001;8:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard J, Martel G, Guillou JL, Nogues X, Micheau J. Impairment of spatial memory consolidation in APP751SL mice results in cue-guided response. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29:1011–1021. - PubMed
-
- Dewachter I, Filipkowski RK, Priller C, Ris L, Neyton J, Croes S, Terwel D, Gysemans M, Devijver H, Borghgraef P, et al. Deregulation of NMDA-receptor function and down-stream signaling in APP[V717I] transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2009;30:241–256. - PubMed
-
- Dickey CA, Gordon MN, Mason JE, Wilson NJ, Diamond DM, Guzowski JF, Morgan D. Amyloid suppresses induction of genes critical for memory consolidation in APP + PS1 transgenic mice. J Neurochem. 2004;88:434–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

