VASP is a CXCR2-interacting protein that regulates CXCR2-mediated polarization and chemotaxis
- PMID: 19435808
- PMCID: PMC2684839
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.039057
VASP is a CXCR2-interacting protein that regulates CXCR2-mediated polarization and chemotaxis
Abstract
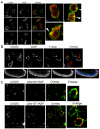
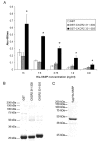
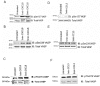
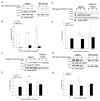
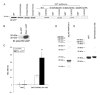
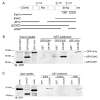
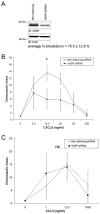
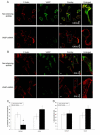
Chemotaxis regulates the recruitment of leukocytes, which is integral for a number of biological processes and is mediated through the interaction of chemokines with seven transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptors. Several studies have indicated that chemotactic signaling pathways might be activated via G-protein-independent mechanisms, perhaps through novel receptor-interacting proteins. CXCR2 is a major chemokine receptor expressed on neutrophils. We used a proteomics approach to identify unique ligand-dependent CXCR2-interacting proteins in differentiated neutrophil-like HL-60 cells. Using this approach, vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) was identified as a CXCR2-interacting protein. The interaction between CXCR2 and VASP is direct and enhanced by CXCL8 stimulation, which triggers VASP phosphorylation via PKA- and PKCdelta-mediated pathways. The interaction between CXCR2 and VASP requires free F-actin barbed ends to recruit VASP to the leading edge. Finally, knockdown of VASP in HL-60 cells results in severely impaired CXCR2-mediated chemotaxis and polarization. These data provide the first demonstration that direct interaction of VASP with CXCR2 is essential for proper CXCR2 function and demonstrate a crucial role for VASP in mediating chemotaxis in leukocytes.
Figures




References
-
- Aszodi, A., Pfeifer, A., Ahmad, M., Glauner, M., Zhou, X. H., Ny, L., Andersson, K. E., Kehrel, B., Offermanns, S. and Fassler, R. (1999). The vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is involved in cGMP- and cAMP-mediated inhibition of agonist-induced platelet aggregation, but is dispensable for smooth muscle function. EMBO J. 18, 37-48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachmann, C., Fischer, L., Walter, U. and Reinhard, M. (1999). The EVH2 domain of the vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein mediates tetramerization, F-actin binding, and actin bundle formation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23549-23557. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw, G. J., Kidd, T., Murray, D., Pawson, T. and Goodman, C. S. (2000). Repulsive axon guidance: Abelson and Enabled play opposing roles downstream of the roundabout receptor. Cell 101, 703-715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK-58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX005225/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- T32CA09592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD-15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54 CA112967-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM058801/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA034590/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-34590/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM-58801/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK-59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY-08126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

