Haploinsufficiency of Krüppel-like factor 5 rescues the tumor-initiating effect of the Apc(Min) mutation in the intestine
- PMID: 19435907
- PMCID: PMC2702486
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4402
Haploinsufficiency of Krüppel-like factor 5 rescues the tumor-initiating effect of the Apc(Min) mutation in the intestine
Abstract
Inactivation of the tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis coli, with the resultant activation of beta-catenin, is the initiating event in the development of a majority of colorectal cancers. Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5), a proproliferative transcription factor, is highly expressed in the proliferating intestinal crypt epithelial cells. To determine whether KLF5 contributes to intestinal adenoma formation, we examined tumor burdens in Apc(Min/+) mice and Apc(Min/+)/Klf5(+/-) mice. Compared with Apc(Min/+) mice, Apc(Min/+)/Klf5(+/-) mice had a 96% reduction in the number of intestinal adenomas. Reduced tumorigenicity in the Apc(Min/+)/Klf5(+/-) mice correlated with reduced levels and nuclear localization of beta-catenin as well as reduced expression of two beta-catenin targets, cyclin D1 and c-Myc. In vitro studies revealed a physical interaction between KLF5 and beta-catenin that enhanced the nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of beta-catenin. Thus, KLF5 is necessary for the tumor-initiating activity of beta-catenin during intestinal adenoma formation in Apc(Min/+) mice, and reduced expression of KLF5 offsets the tumor-initiating activity of the Apc(Min) mutation by reducing the nuclear localization and activity of beta-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
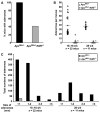
 , ApcMin/+/Klf5+/−. Black horizontal lines, average number of adenomas for each genotype (*, P < 0.001; 16–18 wk, n = 22; 28 wk, n = 11; Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test). C, graph of total numbers of adenomas from mice screened in B, separated by size of adenomas.
, ApcMin/+/Klf5+/−. Black horizontal lines, average number of adenomas for each genotype (*, P < 0.001; 16–18 wk, n = 22; 28 wk, n = 11; Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test). C, graph of total numbers of adenomas from mice screened in B, separated by size of adenomas.



References
-
- Pinto D, Clevers H. Wnt, stem cells and cancer in the intestine. Biol Cell. 2005;97:185–96. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159–70. - PubMed
-
- Moser AR, Pitot HC, Dove WF. A dominant mutation that predisposes to multiple intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Science. 1990;247:322–4. - PubMed
-
- Su LK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, et al. Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene. Science. 1992;256:668–70. - PubMed
-
- Fodde R. The APC gene in colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:867–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

