The NGATHA distal organ development genes are essential for style specification in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 19435933
- PMCID: PMC2700527
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.109.065482
The NGATHA distal organ development genes are essential for style specification in Arabidopsis
Abstract
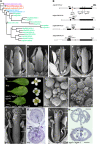
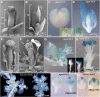
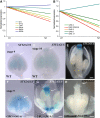
Floral organ identities are specified by a few transcription factors that act as master regulators. Subsequently, specification of organ axes programs the distribution of distinct tissue types within the organs that themselves develop unique identities. The C-class, AGAMOUS-clade MADS box genes are primary promoters of the gynoecium, which is divided into a distal style and a subtending ovary along the apical-basal axis. We show that members of a clade of B3 domain transcription factors, NGATHA1 (NGA1) to NGA4, are expressed distally in all lateral organs, and all four have a redundant and essential role in style development. Loss of all four genes results in gynoecia where style is replaced by valve-like projections and a reduction in style-specific SHATTERPROOF1 (SHP1) expression. In agreement, floral misexpression of NGA1 promotes ectopic style and SHP1 expression. STYLISH1, an auxin biosynthesis inducer, conditionally activated NGA genes, which in turn promoted distal expression of other STY genes in a putative positive feedback loop. Inhibited auxin transport or lack of YABBY1 gene activities resulted in a basally expanded style domain and broader expression of NGA genes. We speculate that early gynoecium factors delimit NGA gene response to an auxin-based signal, elicited by STY gene activity, to restrict the activation of style program to a late and distal carpel domain.
Figures






References
-
- Alvarez, J., and Smyth, D.R. (2002). Crabs Claw and Spatula genes regulate growth and pattern formation during gynoecium development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Plant Sci. 163 17–41.
-
- Balanza, V., Navarrete, M., Trigueros, M., and Ferrandiz, C. (2006). Patterning the female side of Arabidopsis: the importance of hormones. J. Exp. Bot. 57 3457–3469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

