Dynamic behavior of Arabidopsis eIF4A-III, putative core protein of exon junction complex: fast relocation to nucleolus and splicing speckles under hypoxia
- PMID: 19435936
- PMCID: PMC2700535
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.060434
Dynamic behavior of Arabidopsis eIF4A-III, putative core protein of exon junction complex: fast relocation to nucleolus and splicing speckles under hypoxia
Abstract
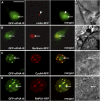
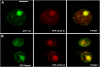
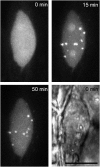
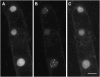
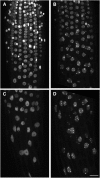
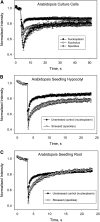
Here, we identify the Arabidopsis thaliana ortholog of the mammalian DEAD box helicase, eIF4A-III, the putative anchor protein of exon junction complex (EJC) on mRNA. Arabidopsis eIF4A-III interacts with an ortholog of the core EJC component, ALY/Ref, and colocalizes with other EJC components, such as Mago, Y14, and RNPS1, suggesting a similar function in EJC assembly to animal eIF4A-III. A green fluorescent protein (GFP)-eIF4A-III fusion protein showed localization to several subnuclear domains: to the nucleoplasm during normal growth and to the nucleolus and splicing speckles in response to hypoxia. Treatment with the respiratory inhibitor sodium azide produced an identical response to the hypoxia stress. Treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 led to accumulation of GFP-eIF4A-III mainly in the nucleolus, suggesting that transition of eIF4A-III between subnuclear domains and/or accumulation in nuclear speckles is controlled by proteolysis-labile factors. As revealed by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching analysis, the nucleoplasmic fraction was highly mobile, while the speckles were the least mobile fractions, and the nucleolar fraction had an intermediate mobility. Sequestration of eIF4A-III into nuclear pools with different mobility is likely to reflect the transcriptional and mRNA processing state of the cell.
Figures



Comment in
-
Localization of eIF4A-III in the nucleolus and splicing speckles is an indicator of plant stress.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 Dec;4(12):1148-51. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.12.9906. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 20514231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alastalo, T.P., Hellesuo, M., Sandqvist, A., Hietakangas, V., Kallio, M., and Sistonen, L. (2003). Formation of nuclear stress granules involves HSF2 and coincides with the nucleolar localization of Hsp70. J. Cell Sci. 116 3557–3570. - PubMed
-
- Ali, G.S., and Reddy, A.S. (2006). ATP, phosphorylation and transcription regulate the mobility of plant splicing factors. J. Cell Sci. 119 3527–3538. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, C.B., Ballut, L., Johansen, J.S., Chamieh, H., Nielsen, K.H., Oliveira, C.L., Pedersen, J.S., Seraphin, B., Le Hir, H., and Andersen, G.R. (2006). Structure of the exon junction core complex with a trapped DEAD-box ATPase bound to RNA. Science 313 1968–1972. - PubMed
-
- Ares, M., Jr., and Proudfoot, N.J. (2005). The spanish connection: transcription and mRNA processing get even closer. Cell 120 163–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

