IDH1 mutations are present in the majority of common adult gliomas but rare in primary glioblastomas
- PMID: 19435942
- PMCID: PMC2743214
- DOI: 10.1215/15228517-2009-025
IDH1 mutations are present in the majority of common adult gliomas but rare in primary glioblastomas
Abstract
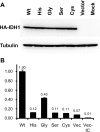
We screened exon 4 of the gene isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (NADP+), soluble (IDH1) for mutations in 596 primary intracranial tumors of all major types. Codon 132 mutation was seen in 54% of astrocytomas and 65% of oligodendroglial tumors but in only 6% of glioblastomas (3% of primary and 50% of secondary glioblastomas). There were no mutations in any other type of tumor studied. While mutations in the tumor protein p53 gene (TP53) and total 1p/19q deletions were mutually exclusive, IDH1 mutations were strongly correlated with these genetic abnormalities. All four types of mutant IDH1 proteins showed decreased enzymatic activity. The data indicate that IDH1 mutation combined with either TP53 mutation or total 1p/19q loss is a frequent and early change in the majority of oligodendroglial tumors, diffuse astrocytomas, anaplastic astrocytomas, and secondary glioblastomas but not in primary glioblastomas.
Figures
References
-
- Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. 4th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2007. - PubMed
-
- Collins VP. Mechanisms of disease: genetic predictors of response to treatment in brain tumors. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2007;4:362–374. - PubMed
-
- Husemann K, Wolter M, Buschges R, Bostrom J, Sabel M, Reifenberger G. Identification of two distinct deleted regions on the short arm of chromosome 1 and rare mutation of the CDKN2C gene from 1p32 in oligodendroglial tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1999;58:1041–1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

