Genetic dissection of an exogenously induced biofilm in laboratory and clinical isolates of E. coli
- PMID: 19436718
- PMCID: PMC2675270
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000432
Genetic dissection of an exogenously induced biofilm in laboratory and clinical isolates of E. coli
Abstract
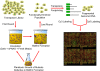
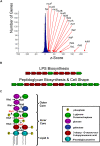
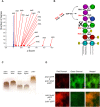
Microbial biofilms are a dominant feature of many human infections. However, developing effective strategies for controlling biofilms requires an understanding of the underlying biology well beyond what currently exists. Using a novel strategy, we have induced formation of a robust biofilm in Escherichia coli by utilizing an exogenous source of poly-N-acetylglucosamine (PNAG) polymer, a major virulence factor of many pathogens. Through microarray profiling of competitive selections, carried out in both transposon insertion and over-expression libraries, we have revealed the genetic basis of PNAG-based biofilm formation. Our observations reveal the dominance of electrostatic interactions between PNAG and surface structures such as lipopolysaccharides. We show that regulatory modulation of these surface structures has significant impact on biofilm formation behavior of the cell. Furthermore, the majority of clinical isolates which produced PNAG also showed the capacity to respond to the exogenously produced version of the polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

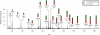
Similar articles
-
PgaB orthologues contain a glycoside hydrolase domain that cleaves deacetylated poly-β(1,6)-N-acetylglucosamine and can disrupt bacterial biofilms.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Apr 23;14(4):e1006998. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006998. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29684093 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine polysaccharide component of Burkholderia biofilms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Dec;77(23):8303-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05814-11. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21984237 Free PMC article.
-
The pgaABCD locus of Acinetobacter baumannii encodes the production of poly-beta-1-6-N-acetylglucosamine, which is critical for biofilm formation.J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(19):5953-63. doi: 10.1128/JB.00647-09. Epub 2009 Jul 24. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19633088 Free PMC article.
-
[Influence of poly-β-1-6-N-acetylglucosamine on biofilm formation and drug resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2015 Feb;31(1):45-7. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25876639 Review. Chinese.
-
Characteristics of the biofilm matrix and its role as a possible target for the detection and eradication of Staphylococcus epidermidis associated with medical implant infections.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010 Aug;59(3):280-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00695.x. Epub 2010 May 12. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20528930 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial adaptation through loss of function.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(7):e1003617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003617. Epub 2013 Jul 11. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23874220 Free PMC article.
-
YajC, a predicted membrane protein, promotes Enterococcus faecium biofilm formation in vitro and in a rat endocarditis model.FEMS Microbes. 2024 May 20;5:xtae017. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtae017. eCollection 2024. FEMS Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38860142 Free PMC article.
-
Dual function of the McaS small RNA in controlling biofilm formation.Genes Dev. 2013 May 15;27(10):1132-45. doi: 10.1101/gad.214734.113. Epub 2013 May 10. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23666921 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated Control of the Assembly and Diversity of LPS by Noncoding sRNAs.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:153561. doi: 10.1155/2015/153561. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26618164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Dispersin B: The Quintessential Antibiofilm Enzyme.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 7;13(8):668. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080668. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick F, Humphreys H, O'Gara JP. The genetics of staphylococcal biofilm formation–will a greater understanding of pathogenesis lead to better management of device-related infection? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005;11:967–973. - PubMed
-
- Izano EA, Wang H, Ragunath C, Ramasubbu N, Kaplan JB. Detachment and killing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans biofilms by dispersin B and SDS. J Dent Res. 2007;86:618–622. - PubMed

