Molecular mechanics of the alpha-actinin rod domain: bending, torsional, and extensional behavior
- PMID: 19436721
- PMCID: PMC2676514
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000389
Molecular mechanics of the alpha-actinin rod domain: bending, torsional, and extensional behavior
Abstract
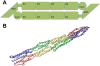
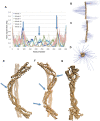
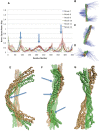
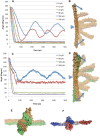
alpha-Actinin is an actin crosslinking molecule that can serve as a scaffold and maintain dynamic actin filament networks. As a crosslinker in the stressed cytoskeleton, alpha-actinin can retain conformation, function, and strength. alpha-Actinin has an actin binding domain and a calmodulin homology domain separated by a long rod domain. Using molecular dynamics and normal mode analysis, we suggest that the alpha-actinin rod domain has flexible terminal regions which can twist and extend under mechanical stress, yet has a highly rigid interior region stabilized by aromatic packing within each spectrin repeat, by electrostatic interactions between the spectrin repeats, and by strong salt bridges between its two anti-parallel monomers. By exploring the natural vibrations of the alpha-actinin rod domain and by conducting bending molecular dynamics simulations we also predict that bending of the rod domain is possible with minimal force. We introduce computational methods for analyzing the torsional strain of molecules using rotating constraints. Molecular dynamics extension of the alpha-actinin rod is also performed, demonstrating transduction of the unfolding forces across salt bridges to the associated monomer of the alpha-actinin rod domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spectrin-like repeats from dystrophin and alpha-actinin-2 are not functionally interchangeable.Hum Mol Genet. 2002 Aug 1;11(16):1807-15. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.16.1807. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. PMID: 12140183
-
Structural analysis of homologous repeated domains in alpha-actinin and spectrin.Int J Biol Macromol. 1989 Apr;11(2):81-90. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(89)90047-0. Int J Biol Macromol. 1989. PMID: 2489070
-
Crystal structure of the alpha-actinin rod reveals an extensive torsional twist.Structure. 2001 Jul 3;9(7):597-604. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00619-0. Structure. 2001. PMID: 11470434
-
The spectrin repeat: a structural platform for cytoskeletal protein assemblies.FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):119-23. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03304-x. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11911890 Review.
-
Alpha-actinin and spectrin structures: an unfolding family story.FEBS Lett. 1999 Nov 5;460(3):391-4. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01372-1. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10556504 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel ACTN1 variants in cases of thrombocytopenia.Hum Mutat. 2019 Dec;40(12):2258-2269. doi: 10.1002/humu.23840. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 31237726 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation primes vinculin for activation.Biophys J. 2012 May 2;102(9):2022-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.01.062. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 22824265 Free PMC article.
-
Marking and measuring single microtubules by PRC1 and kinesin-4.Cell. 2013 Jul 18;154(2):377-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.021. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23870126 Free PMC article.
-
Electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction evidence for two Z-band structural states.Biophys J. 2011 Aug 3;101(3):709-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.06.024. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21806939 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing dynamic cytoplasmic forces with a compliance-matched FRET sensor.J Cell Sci. 2011 Jan 15;124(Pt 2):261-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.071928. Epub 2010 Dec 20. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21172803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanchard A, Ohanian V, Critchley D. The structure and function of alpha-actinin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989;10:280–289. - PubMed
-
- Fraley TS, Pereira CB, Tran TC, Singleton C, Greenwood JA. Phosphoinositide binding regulates alpha-actinin dynamics: mechanism for modulating cytoskeletal remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:15479–15482. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

