Regulation of ErbB2 receptor status by the proteasomal DUB POH1
- PMID: 19436748
- PMCID: PMC2677670
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005544
Regulation of ErbB2 receptor status by the proteasomal DUB POH1
Abstract
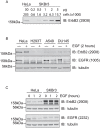
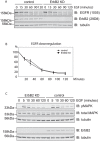
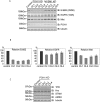
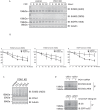
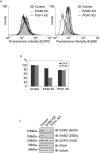
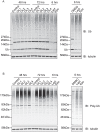
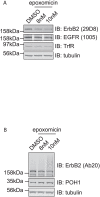
Understanding the factors, which control ErbB2 and EGF receptor (EGFR) status in cells is likely to inform future therapeutic approaches directed at these potent oncogenes. ErbB2 is resistant to stimulus-induced degradation and high levels of over-expression can inhibit EGF receptor down-regulation. We now show that for HeLa cells expressing similar numbers of EGFR and ErbB2, EGFR down-regulation is efficient and insensitive to reduction of ErbB2 levels. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) may extend protein half-lives by rescuing ubiquitinated substrates from proteasomal degradation or from ubiquitin-dependent lysosomal sorting. Using a siRNA library directed at the full complement of human DUBs, we identified POH1 (also known as Rpn11 or PSMD14), a component of the proteasome lid, as a critical DUB controlling the apparent ErbB2 levels. Moreover, the effects on ErbB2 levels can be reproduced by administration of proteasomal inhibitors such as epoxomicin used at maximally tolerated doses. However, the extent of this apparent loss and specificity for ErbB2 versus EGFR could not be accounted for by changes in transcription or degradation rate. Further investigation revealed that cell surface ErbB2 levels are only mildly affected by POH1 knock-down and that the apparent loss can at least partially be explained by the accumulation of higher molecular weight ubiquitinated forms of ErbB2 that are detectable with an extracellular but not intracellular domain directed antibody. We propose that POH1 may deubiquitinate ErbB2 and that this activity is not necessarily coupled to proteasomal degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

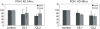
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of human deubiquitinase PSMD14 induces cell cycle arrest and senescence.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Jan 15;316(2):258-71. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.08.018. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 19732767
-
The JAMM motif of human deubiquitinase Poh1 is essential for cell viability.Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Jan;6(1):262-8. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0542. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17237285
-
Novel insights into the non-canonical roles of PSMD14/POH1/Rpn11 in proteostasis and in the modulation of cancer progression.Cell Signal. 2023 Jan;101:110490. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110490. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Cell Signal. 2023. PMID: 36241058
-
POH1/Rpn11/PSMD14: a journey from basic research in fission yeast to a prognostic marker and a druggable target in cancer cells.Br J Cancer. 2022 Sep;127(5):788-799. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01829-z. Epub 2022 May 2. Br J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35501388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trimming of ubiquitin chains by proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzymes.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 May;10(5):R110.003871. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R110.003871. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 20823120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UCHL5 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Cancer Cells by Activating c-Myc via AKT/mTOR Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;14(22):5538. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225538. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428630 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered bivalent ligands to bias ErbB receptor-mediated signaling and phenotypes.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 5;286(31):27729-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.221093. Epub 2011 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21622572 Free PMC article.
-
Degradome-focused RNA interference screens to identify proteases important for breast cancer cell growth.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 12;12:960109. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.960109. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313646 Free PMC article.
-
Protease addiction and synthetic lethality in cancer.Front Oncol. 2011 Sep 5;1:25. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2011.00025. eCollection 2011. Front Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22655236 Free PMC article.
-
POH1 deubiquitylates and stabilizes E2F1 to promote tumour formation.Nat Commun. 2015 Oct 29;6:8704. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9704. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26510456 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

