Analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD8 T-cells in patients with active tuberculosis and in individuals with latent infection
- PMID: 19436760
- PMCID: PMC2678250
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005528
Analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD8 T-cells in patients with active tuberculosis and in individuals with latent infection
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific CD8 T-Cells in Patients with Active Tuberculosis and in Individuals with Latent Infection.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 19;14(9):e0223028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223028. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31536598 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
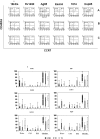
CD8 T-cells contribute to control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, but little is known about the quality of the CD8 T-cell response in subjects with latent infection and in patients with active tuberculosis disease. CD8 T-cells recognizing epitopes from 6 different proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis were detected by tetramer staining. Intracellular cytokines staining for specific production of IFN-gamma and IL-2 was performed, complemented by phenotyping of memory markers on antigen-specific CD8 T-cells. The ex-vivo frequencies of tetramer-specific CD8 T-cells in tuberculous patients before therapy were lower than in subjects with latent infection, but increased at four months after therapy to comparable percentages detected in subjects with latent infection. The majority of CD8 T-cells from subjects with latent infection expressed a terminally-differentiated phenotype (CD45RA+CCR7(-)). In contrast, tuberculous patients had only 35% of antigen-specific CD8 T-cells expressing this phenotype, while containing higher proportions of cells with an effector memory- and a central memory-like phenotype, and which did not change significantly after therapy. CD8 T-cells from subjects with latent infection showed a codominance of IL-2+/IFN-gamma+ and IL-2(-)/IFN-gamma+ T-cell populations; interestingly, only the IL-2+/IFN-gamma+ population was reduced or absent in tuberculous patients, highly suggestive of a restricted functional profile of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific CD8 T-cells during active disease. These results suggest distinct Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific CD8 T-cell phenotypic and functional signatures between subjects which control infection (subjects with latent infection) and those who do not (patients with active disease).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Control: Surveillance, Planning, Financing. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008. Available at http://www.who.int/entity/tb/publications/global_report/2008/pdf/fullrep....
-
- Koga T, Wand-Wurttenberger A, DeBruyn J, Munk ME, Schoel B, et al. T cells against a bacterial heat shock protein recognize stressed macrophages. Science. 1989;4922:1112–1115. - PubMed
-
- Stenger S, Mazzaccaro RJ, Uyemura K, Cho S, Barnes PF, et al. Differential effects of cytolytic T cell subsets on intracellular infection. Science. 1997;276:1684–1687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

